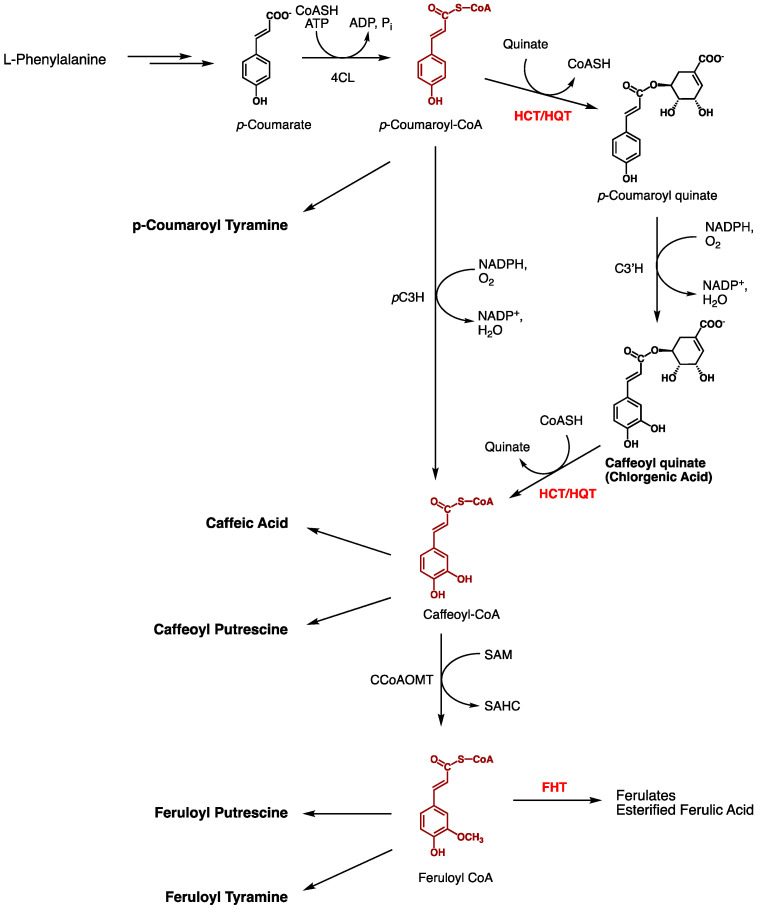
Figure 10.
Phenylpropanoid metabolism. The origin of suberin-derived phenylpropanoids is shown, highlighting the placement of StHCT and StFHT. StFHT catalyzes the transfer of ferulic acid moieties from feruloyl-CoA to acyl acceptors (i.e., ferulates) and suberin aliphatic monomers (i.e., yielding esterified ferulic acid). In contrast, StHCT is hypothesized to transfer p-coumaric acid moieties from p-coumaroyl-CoA to quinate (or shikimate) acceptors prior to their hydroxylation to form caffeoyl quinate(shikimate) via p-coumaroyl quinate-3′-hydroxylase (C3′H). The caffeoyl moiety from caffeoyl quinate is then transferred to CoASH by the reverse StHCT reaction. The CoA derivatives of p-coumaric, caffeic, and ferulic acids are hypothesized to be precursors to the putrescine and tyramine amides that accumulate in potato tubers post-wounding. Names of compounds found to accumulate in StFHT- and StHCT-RNAi lines are in boldface type. Abbreviations: 4CL, 4-coumaroyl-CoA ligase; pC3H, p-coumarate-3-hydroxylase; HCT/HQT, hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA shikimate/quinate hydroxycinnamoyl transferase; C3′H, p-coumaroyl quinate-3′-hydroxylase; CCoAOMT, caffeoyl-CoA O-methyl transferase; FHT, fatty ω-hydroxyacid/fatty alcohol hydroxycinnamoyl transferase.