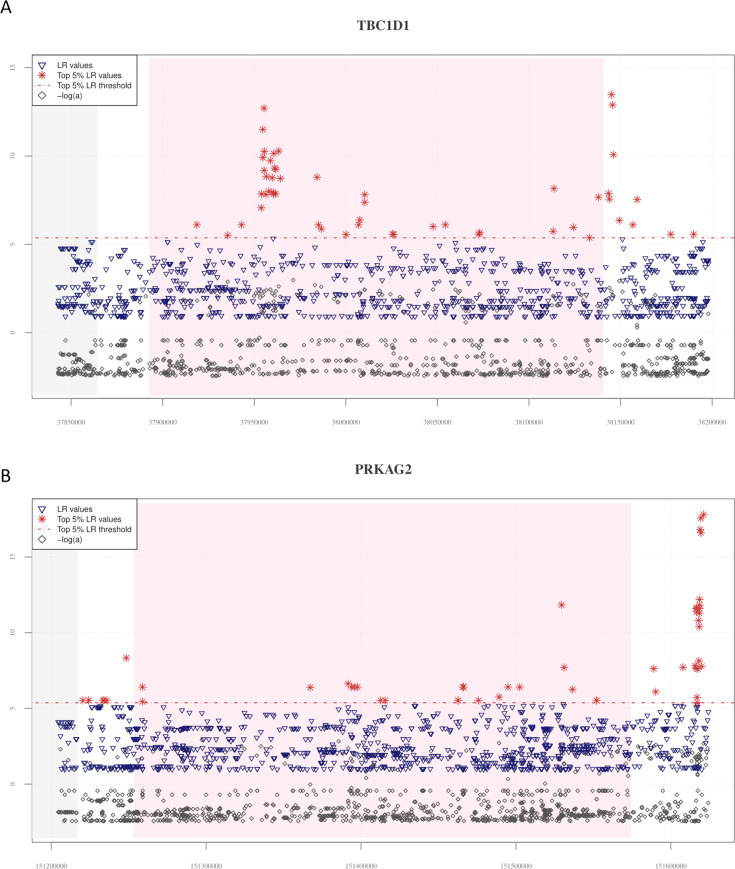
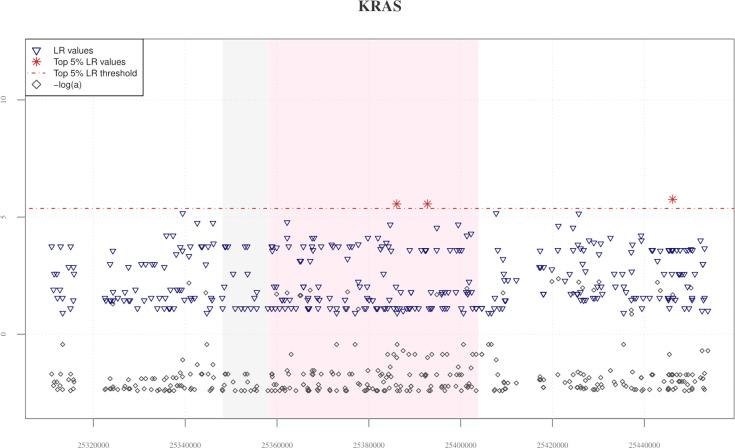
Figure 2. Distribution of VolcanoFinder statistics suggestive of putative adaptive introgrossed loci across the TBC1D1 and PRKAG2 genomic regions.
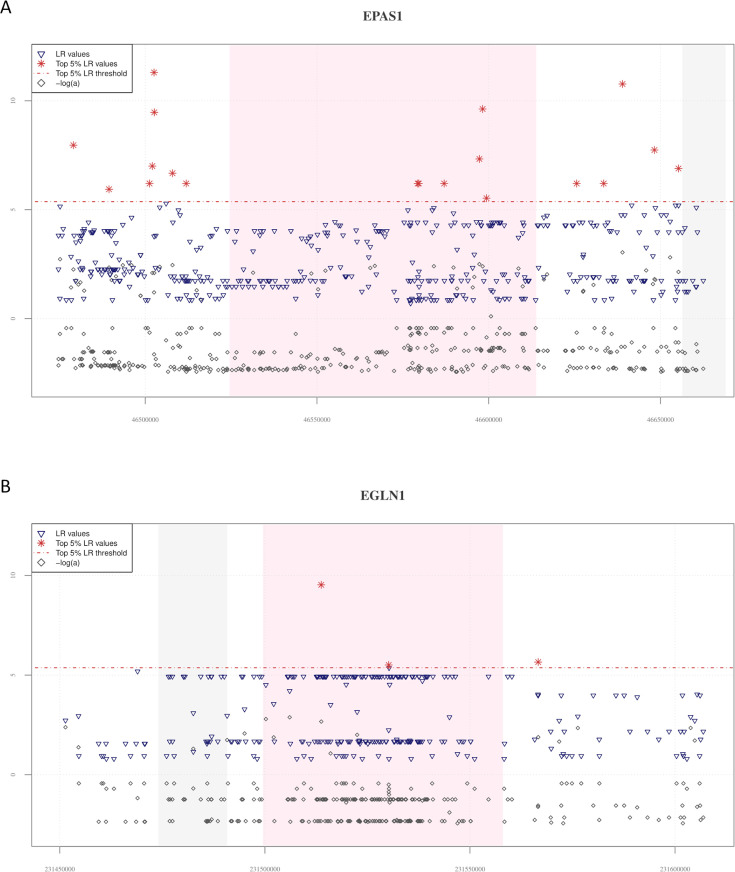
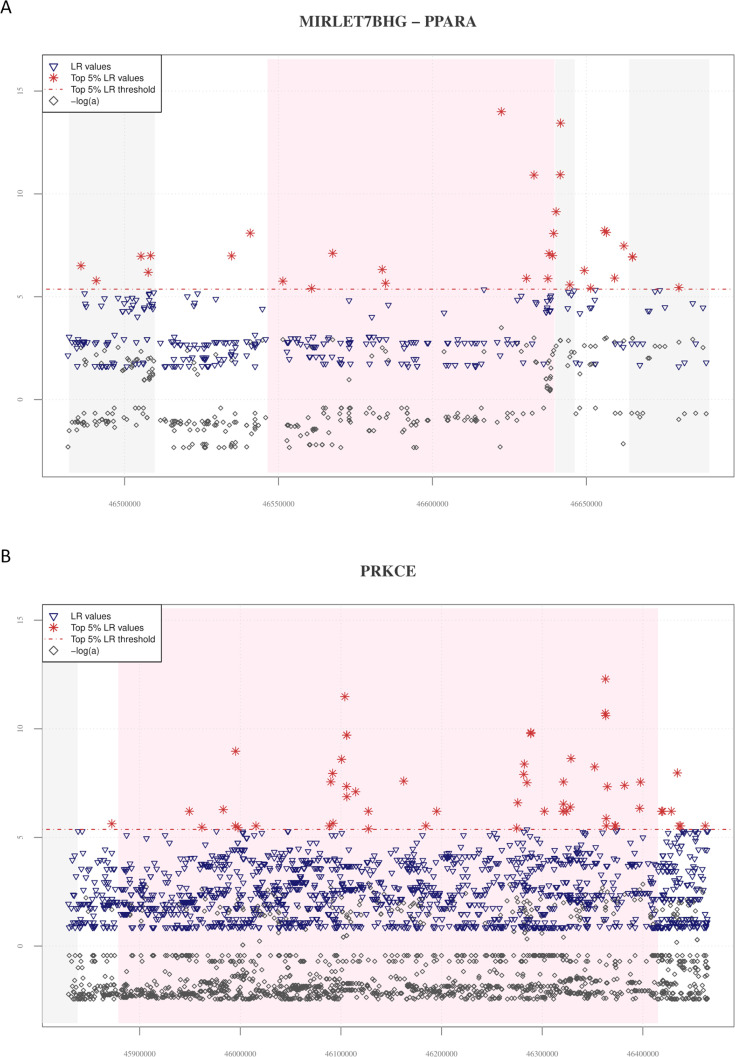
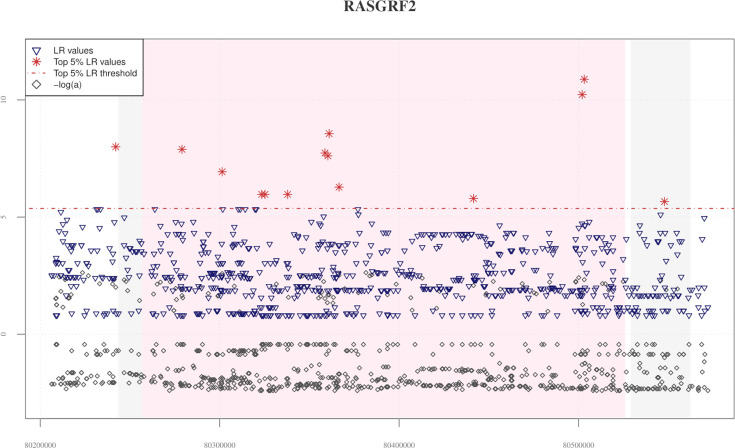
On the x-axis are reported genomic positions of each single-nucleotide variant (SNV), while on the y-axis are displayed the related statistics obtained. Pink background indicates the chromosomal interval occupied by the considered genes, while the grey background identifies those genes (i.e., PGM2 in the TBC1D1 downstream genomic region and the RHEB gene in the upstream PRKAG2 region) possibly involved in regulatory transcription mechanisms. The dashed red line identifies the threshold set to filter for significant likelihood ratio (LR) values (i.e., top 5% of LR values). For both these genomic regions, the distribution of LR and −logα are concordant with those observed at the EPAS1 positive control for adaptive introgression (AI). (A) A total of 50 significant LR values (red stars) and −logα (grey diamonds) values resulted collectively elevated in both the TBC1D1 gene and its downstream genomic regions. A remarkable concentration of significant LR values characterizing 19 SNVs was especially observable in the first portion of the gene. (B) The entire PRKAG2 genomic region was found to comprise 46 SNVs showing significant LR values, with the greatest peaks being located in the downstream region associated to such gene. Peaks detected for the LR statistic are accompanied by peaks of −logα values.