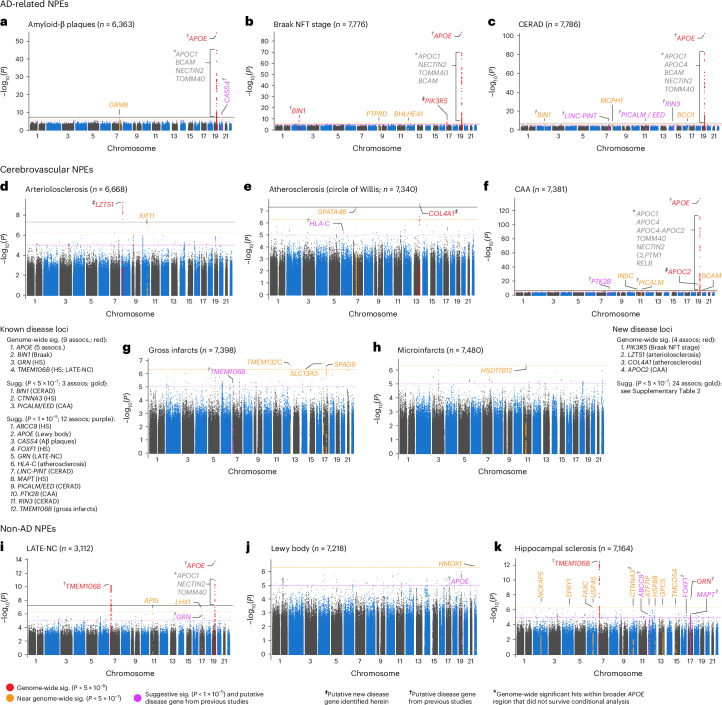
Fig. 2. Manhattan plots identify loci associated with each of the 11 NPEs included in this study.
a–k, Manhattan plots are shown for amyloid-β plaques (a), Braak NFT stage (b), CERAD score for neuritic plaques (c), arteriolosclerosis (d), atherosclerosis in the circle of Willis (e), CAA (f), gross infarcts (g), microinfarcts (h), LATE-NC (i), Lewy body (j) and hippocampal sclerosis (k). The y axes denote the −log10(P value of meta-analysis two-sided z test) of the variant–phenotype association, and the x axes outline the chromosomal position, with alternate chromosomes represented in black and blue. Labels indicate the nearest gene at a locus. The horizontal lines define the genome-wide significance level (solid black, P = 5 × 10−8), near genome-wide significance level (dotted gold, P = 5 × 10−7), and suggestive significance level (P < 5 × 10−5) in loci with evidence of AD association from a previous study (for example, ref. 6; dotted purple). Points and gene symbols are coded with the same colors. Gray gene symbols indicate genome-wide significant hits within the APOE region that did not survive conditional analysis. All GWAS are in cohorts of European ancestry and adjusted for age at death, sex, genotyping cohort and top ten genetic PCs. We identified eight genome-wide significant loci and 39 near genome-wide significant or suggestive loci. The genome-wide significant loci resulted in 14 associations with eight NPEs (amyloid-β plaques, arteriolosclerosis, atherosclerosis, Braak NFT stage, CAA, CERAD score, hippocampal sclerosis and LATE-NC). Four genes were previously associated with ADRD (APOE, BIN1, TMEM106B, GRN; a–c,f,i,k), while the four new loci were in or closest to PIK3R5, LZTS1, COL4A1 and APOC2 (b,d,e,f). APOC2 is within the broader APOE region but remained significantly associated with CAA after adjusting for APOE diplotypes (f). Three NPEs (gross infarcts, microinfarcts and Lewy bodies) had zero genome-wide significant hits, but all three had near genome-wide significant and/or suggestive hits from either new or known loci. APOE was associated with a range of NPEs, including LATE-NC, which is not pathognomonic of AD. On the other hand, neither GRN nor TMEM106B (recently identified in ADRD GWAS) was associated with the AD pathognomonic NPEs but were specific to gross infarcts, LATE-NC and hippocampal sclerosis at either genome-wide or suggestive significance. sig., significant; assocs, associations; sugg., suggestive.