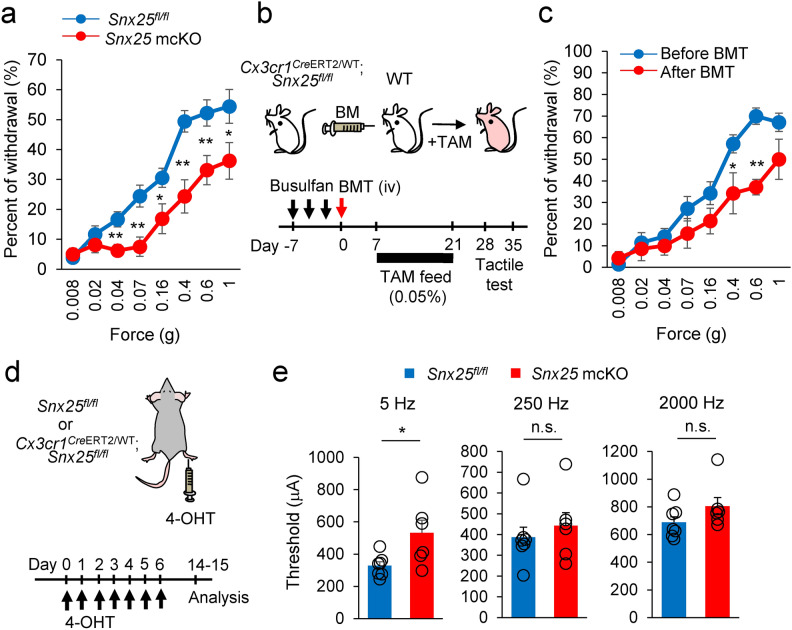
Fig. 2.
Snx25 mcKO yields a tactile-insensitive phenotype. (a) Fine tactile sensitivity was examined with von Frey filaments whose mechanical pressure ranged from 0.008 g to 1 g. The percentages of withdrawal (positive response) to innocuous low-pressure stimuli were plotted (Snx25fl/fl mice: n = 18; Snx25 mcKO mice: n = 16). 0.04g; p = 0.004, 0.07g; p = 0.002, 0.16g; p = 0.024, 0.4g; p = 0.0005, 0.6g; p = 0.006, 1.0g; p = 0.036. (b) Schedules for generation of BM chimeric mice by transplanting Snx25 mcKO BM into WT mice, and subsequent tactile test. (c) Tactile test in chimeric mice (Snx25 mcKO BM → WT: n = 7, 35 days after BMT). 0.4g; p = 0.048, 0.6g; p = 3.955e-05. (d) Scheme depicting dermal injection of 4-OHT into hind paws of a Cx3cr1CreERT2/WT; Snx25fl/fl mouse and experimental time course. To achieve gene recombination, we injected 4-OHT daily for 7 days and evaluated responses of sensory afferent fibers using transcutaneous sine wave stimuli at 8–9 days after the last injection. (e) Paw withdrawal thresholds in response to sine-wave electrical stimuli in Snx25 mcKO mice. The current threshold represents the minimum intensity (μA) required to produce a paw withdrawal response with sine-wave electrical stimulation at 5, 250, and 2000 Hz (Snx25fl/fl mice: n = 7; Snx25 mcKO mice: n = 6). 5Hz; p = 0.033, 250Hz; p = 0.525, 2000Hz; p = 0.171. The data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n.s., not significant. Results are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using the Student’s t-test.