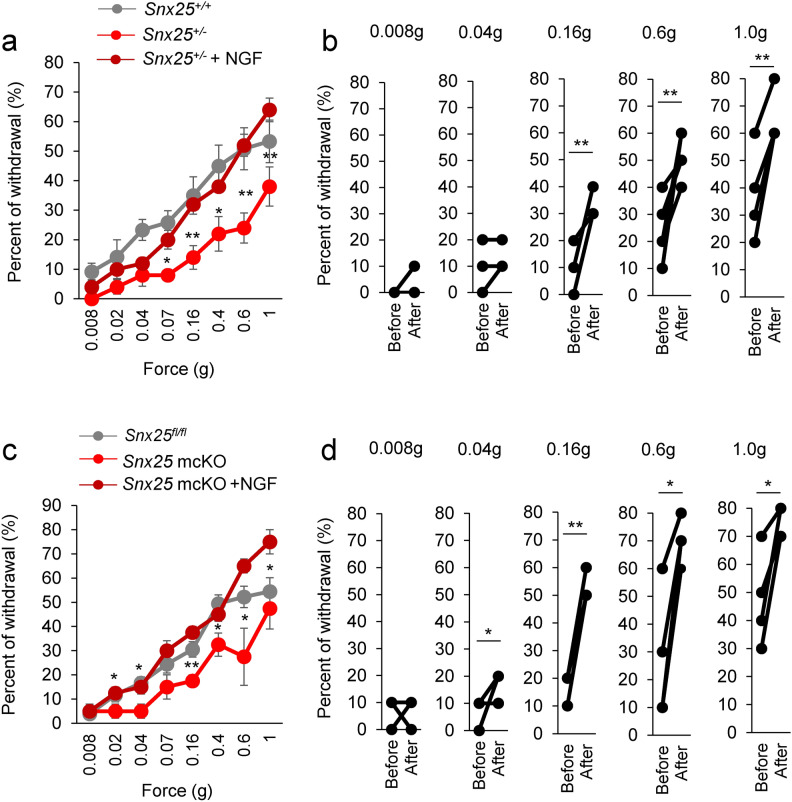
Fig. 7.
Dull phenotype of tactile sensitivity is rescued by intradermal injection of NGF. (a) Fine tactile sensitivity was examined with von Frey filaments whose mechanical pressure ranged from 0.008 g to 1 g, in Snx25+/- mice and in Snx25+/- mice at 24 h after NGF injection (n = 5). 0.07g; p = 0.012, 0.16g; p = 0.004, 0.4g; p = 0.032, 0.6g; p = 0.002, 1.0g; p = 0.001. (b) Changes of percent of withdrawal on the side injected with NGF of each Snx25+/- mouse (n = 5). 0.16g; p = 0.004, 0.6g; p = 0.002, 1.0g; p = 0.001. (c) Fine tactile sensitivity was examined with von Frey filaments as above, in Snx25 mcKO mice and in Snx25 mcKO mice at 24 h after NGF injection (n = 4). 0.02g; p = 0.017, 0.04g; p = 0.017, 0.16g; p = 6.14e-05, 0.4g; p = 0.001, 0.6g; p = 0.015, 1.0g; p = 0.022. (d) Changes of percent of withdrawal on the side injected with NGF of each Snx25 mcKO mouse (n = 4). 0.04g; p = 0.017, 0.16g; p = 6.14e-05, 0.6g; p = 0.015, 1.0g; p = 0.022.*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Results are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using the Student’s t-test (Snx25+/- vs Snx25+/- + NGF, or Snx25 mcKO vs Snx25 mcKO + NGF).