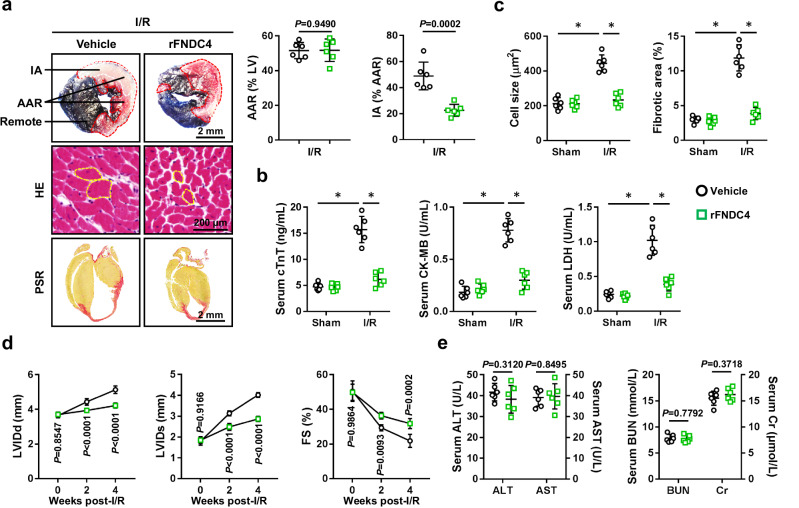
Fig. 8. Therapeutic administration of rFNDC4 protein is sufficient to attenuate cardiac I/R injury.
a Evans blue and TTC double staining was performed to identify the IA, AAR and remote area of heart samples 24 h after I/R surgery. Circles indicate the cross-sectional area of cardiomyocytes (n = 6). b Serum levels of cTnT, creatine kinase isoenzymes (CK-MB) and LDH in I/R-stressed mice with or without recombinant FNDC4 (rFNDC4) protein treatment (n = 6). c Heart samples with or without rFNDC4 protein treatment were collected 4 weeks after I/R surgery and subjected to HE and PSR staining, and cell size as well as fibrotic area were quantified (n = 6). d Cardiac function of rFNDC4- or vehicle-treated mice was analyzed by transthoracic echocardiography at the indicated time points (n = 6). (e) Serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (Cr) (n = 6 biological samples). Data were presented as the mean ± S.D., and analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test. For the analysis in (a–e), an unpaired two-tailed Student′s t-test was used. For the analysis in (d), repeated measures ANOVA was performed. *P < 0.0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.