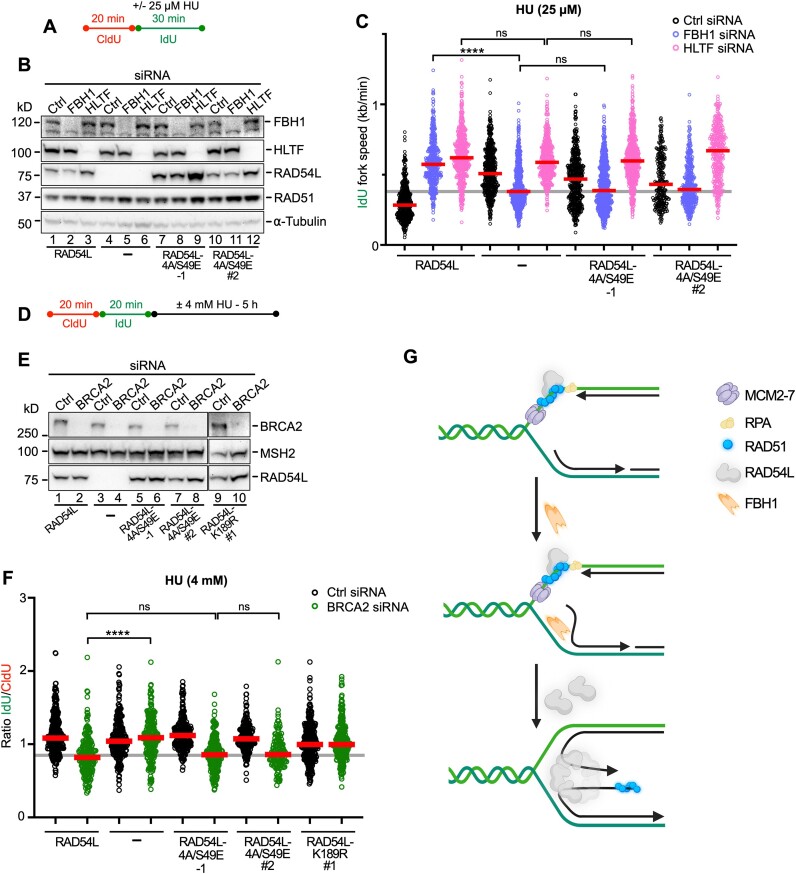
Figure 6.
RAD54L’s branch migration activity is specifically required for the FBH1 pathway of RAD51-mediated fork reversal. (A) Schematic of the DNA fiber assay protocol used in (C). (B) Representative Western blots to show extent of FBH1 and HLTF knockdown in RAD54L KO cells (lanes 4–6) and RAD54L KO cells expressing wild type RAD54L (lanes 1–3) or mutant RAD54L-4A/S49E (lanes 7–12). RAD54L-4A/S49E-1 dignifies a clonal isolate; RAD54L-4A/S49E #2 dignifies a puromycin-resistant cell population. Loading control: α-tubulin. (C) Dot plot with medians of IdU fork speeds in HU-treated RAD54L KO cells and RAD54L KO cells expressing wild type RAD54L or RAD54L-4A/S49E and transfected with Ctrl, FBH1 or HLTF siRNA (n = 3; 85–224 fiber tracts/experiment analyzed; n = 1 for RAD54L-4A/S49E #2). (D) Schematic of the DNA fiber assay protocol used in (F). (E) Representative western blots to show extent of BRCA2 knockdown in RAD54L KO cells (lanes 3–4) and RAD54L KO cells expressing wild type RAD54L (lanes 1–2) or mutant RAD54L-4A/S49E (lanes 5–8) and RAD54L-K189R (lanes 9–10). RAD54L-4A/S49E-1 dignifies a clonal isolate; RAD54L-4A/S49E #2 and RAD54L-K189R #1 dignifies puromycin-resistant cell populations. Loading control: MSH2. (F) Dot plot with medians of IdU/CldU tract length ratios in HU-treated RAD54L KO cells and RAD54L KO cells expressing wild type RAD54L or mutant RAD54L-4A/S49E and RAD54L-K189R transfected with Ctrl or BRCA2 siRNA (n = 3; 46–104 fiber tracts/experiment analyzed; n = 1 for RAD54L-K189R #1). Data were analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test (ns, not significant; ∗∗∗∗P< 0.0001). (G) Model to explain the role of RAD54L in the FBH1 pathway of RAD51-mediated fork reversal. RAD54L may be recruited through its interaction with RAD51 on extended parental ssDNA. FBH1 is recruited to stalled replication forks by PCNA ((78); PCNA is not shown here). Unwinding of lagging strand DNA through FBH1 (72) may initiate nascent strand annealing. RAD54L may then oligomerize on a 4-way junction and drive reversal through BM. The dependency of FBH1 on RAD54L may be indicative of coordinated recruitment and/or post-translational modification orchestrating sequential coaction. The number of subunits in the RAD54L BM oligomer remain to be determined. Schematic created with Biorender.com.