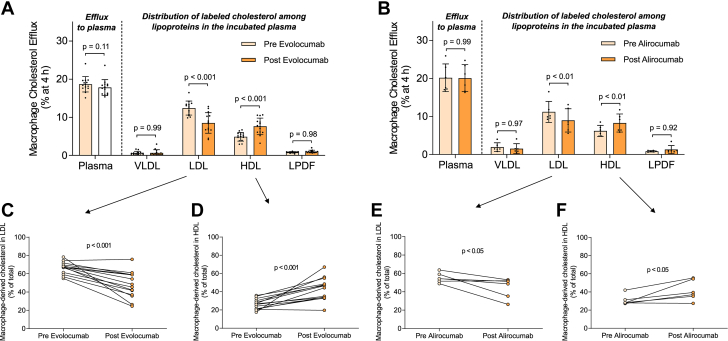
Figure 1.
Anti-PCSK9 Therapies Modify the Ability of LDL and HDL to Function as Macrophage Cholesterol Acceptors Ex Vivo
J774A.1 macrophages were exposed to media containing plasma (2.5% vol/vol) obtained from 14 heterozygous FH subjects before and after treatment with evolocumab (A) or from 6 individual heterozygous FH subjects before and after treatment with alirocumab (B) in cholesterol efflux assays. The distribution of radiolabeled cholesterol in the indicated lipoprotein fractions of the incubated plasma was determined after isolating the lipoproteins through sequential density ultracentrifugation. The percentage of the total radiolabeled cholesterol accumulated in LDL is presented as matched pairs for evolocumab (C) and alirocumab-treated (E) plasmas. The percentage of the total radiolabeled cholesterol accumulated in HDL is depicted as matched pairs for evolocumab (D) and alirocumab-treated (F) plasmas. Values in A and B are expressed as mean ± SD. A repeated measures 2-way analysis of variance followed by Šídák multiple comparison test was conducted to compare macrophage cholesterol efflux with plasma and the amount of radiolabeled cholesterol in VLDL, LDL, HDL, and LPDF. A paired t-test was performed to compare macrophage-derived cholesterol in LDL and HDL. FH = familial hypercholesterolemia; HDL = high-density lipoprotein; LDL = low-density lipoprotein; LPDF = lipoprotein-deleted fraction.