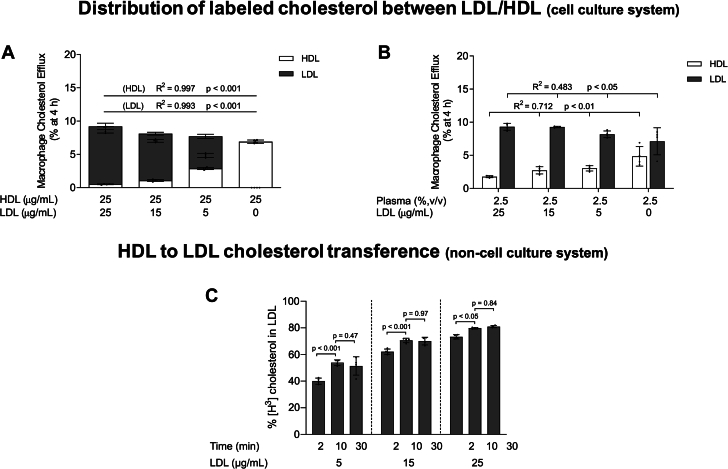
Figure 2.
The Capacity of HDL to Serve as a Macrophage Cholesterol Acceptor Is Enhanced Through Coincubation With Low LDL Levels In Vitro
(A) In vitro cholesterol efflux from J774A.1 macrophages stimulated by HDL (25 μg/mL of APOA1) in the absence or presence of LDL added to the culture media at concentrations up to 25 μg/mL (APOB100). The distribution of labeled cholesterol between LDL and HDL was evaluated after precipitation of LDL with phosphotungstic acid-MgCl2. (B) In vitro cholesterol efflux from J774A.1 macrophages stimulated by plasma (2.5% vol/vol) in the absence or presence of LDL added to the culture media at concentrations up to 25 μg/mL (APOB100). The distribution of radiolabeled cholesterol in the lipoprotein fractions was determined after isolating the lipoproteins by sequential density ultracentrifugation. For (A) and (B), ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by a post-test for linear trend was performed to compare the accumulation of radiolabeled cholesterol in LDL and HDL. (C) Distribution of labeled cholesterol during the incubation of radiolabeled HDL isolated from cell culture media with increased concentrations of unlabeled LDL for 2, 10, and 30 minutes in a cell-free system. The amount of [3H]cholesterol in HDL and LDL was determined after precipitation of LDL with phosphotungstic acid-MgCl2. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments in each condition. Two-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was performed to compare the different incubation times for each LDL concentration. Two-way ANOVA results were time, P < 0.001; LDL concentration, P < 0.001. ANOVA = analysis of variance; APO = apolipoprotein; other abbreviations as in Figure 1.