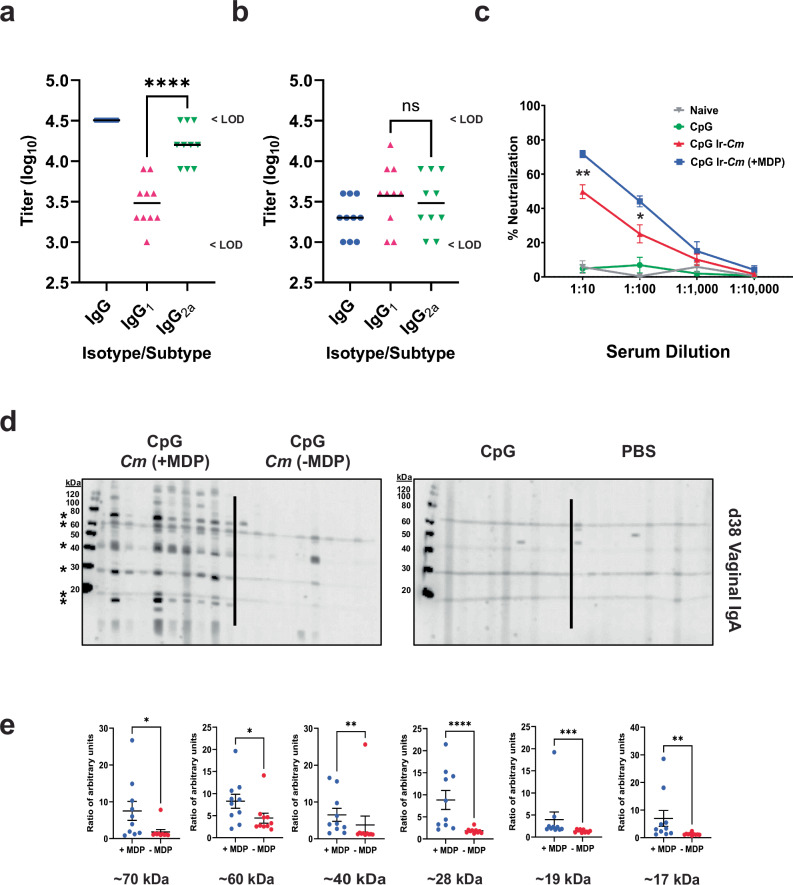
Fig. 2. A whole-cell Cm vaccine irradiated in the presence of MDP (Ir-Cm + MDP) induces Chlamydia-specific and functional antibody responses.
a, b ELISA titers of d38 serum from individual mice comprising the Ir-Cm (+MDP) (a) and Ir-Cm (−MDP) (b) immunization groups. For the purpose of carrying out a statistical analysis, LOD values were used. Differences between isotypes/subtypes were assessed via one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. ****p < 0.0001, ns not significant. c Serum neutralization assays comparing pooled serum from the same groups of animals presented in (a–b). Data points represent four separate neutralization assays from the same pooled sera stocks (collected on d38) using freshly isolated infectious EBs. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. The 1:10 and 1:100 serum dilutions were compared between the CpG IR-Cm and CpG IR-Cm + MDP groups via one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05. d Western blots against fractionated Cm EB lysates showing vaginal Cm-specific IgA from individual mice vaccinated with Cm irradiated (Ir-Cm) in the presence or absence of MDP, adjuvant (CpG) alone, or PBS (naïve mice). Vaginal washes were collected on d38; 10 days after the final immunization and tested via WB at a 1:200 dilution. Solid black lines are used to delineate between experimental groups on WBs. e Quantitative band intensity analysis for the six most prominent bands from western blots presented in (d), (as indicated by asterisks). The mid-line indicates the mean of all data points and the error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Significance was assessed via the Mann–Whitney test. ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.