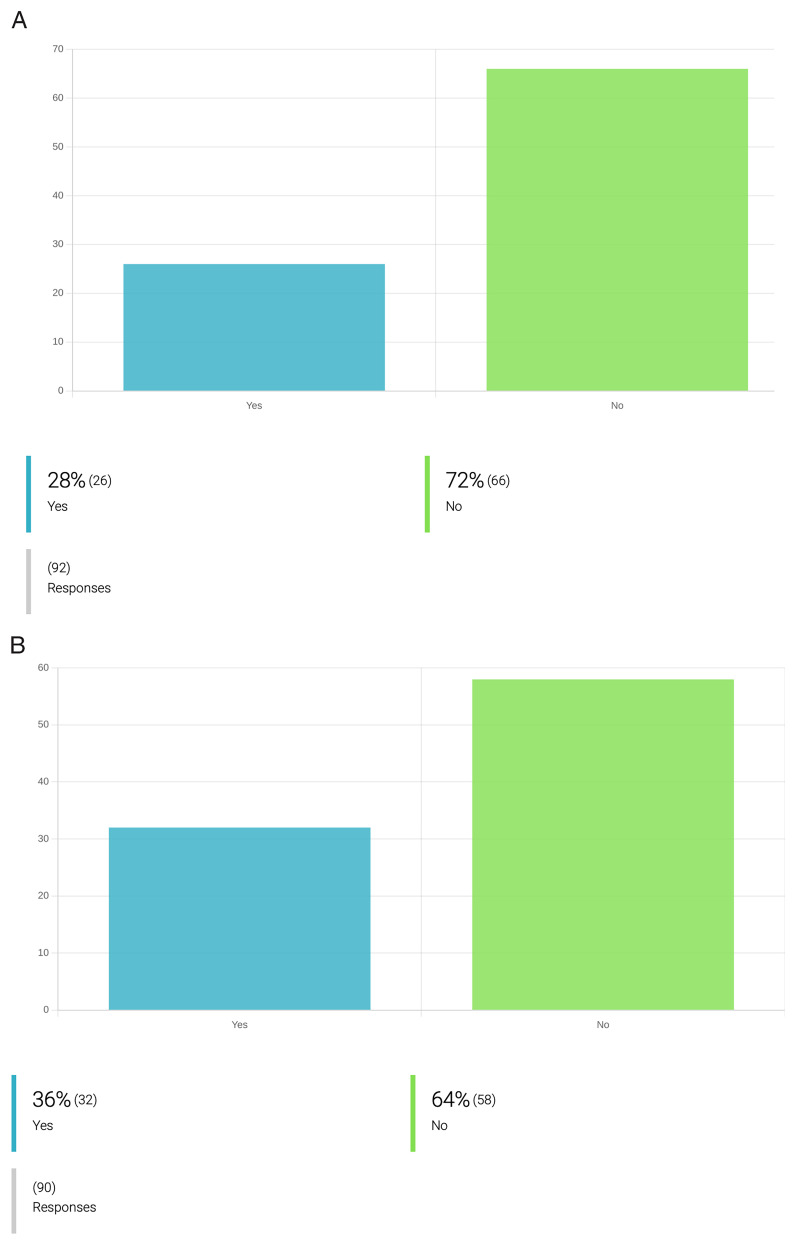
Figure 5. Attitudes and practices to mitigate water, energy and plastic consumption during drug development for PVBD.
A. Incorporation of measures to reduce plastic use during the process of drug development against PVBDs. B. Incorporation of measures to reduce energy consumption during the process of drug development against PVBDs.
Only 28% of the inquired researchers employ strategies to reduce plastic use during their research activities. These include: recycling, replacement of plastic materials by glass (ex. glass pipettes, glass wire; glass TLC plates; glass tubes); reduce the use of single plastic use equipment; optimize experiments to reduce waste production and plastic consumption (e.g. optimize the use of 96-well plates to fill all spaces available); recycle solvents; clean and re-use plastic for enzyme kinetics assays; replace plastic spectroscopic cuvettes by glass cuvettes. Regarding measures to reduce electricity consumption, only 36% of the inquired researchers employ at least one measure. These include: ultra-sound assisted synthesis, microwave-assisted synthesis (ex. MAOS); multicomponent reactions; limiting unnecessary illumination outside the normal working hours (e.g. lights off when the room is not used); limiting unnecessary heating outside the normal working hours; privileging the use of instruments with low energy consumption; routine inspection and maintenance of freezers (-20°C and -80°C) to avoid frost); selection of chemical synthesis protocols that involve milder conditions, with less energy consumption; implementation of institutional attitudes and practices that allow energy saving (e.g. new architectural designs of research buildings with energy saving systems); reducing the number of equipment kept on standby for long time; disconnect appliances and lab instruments when not used.