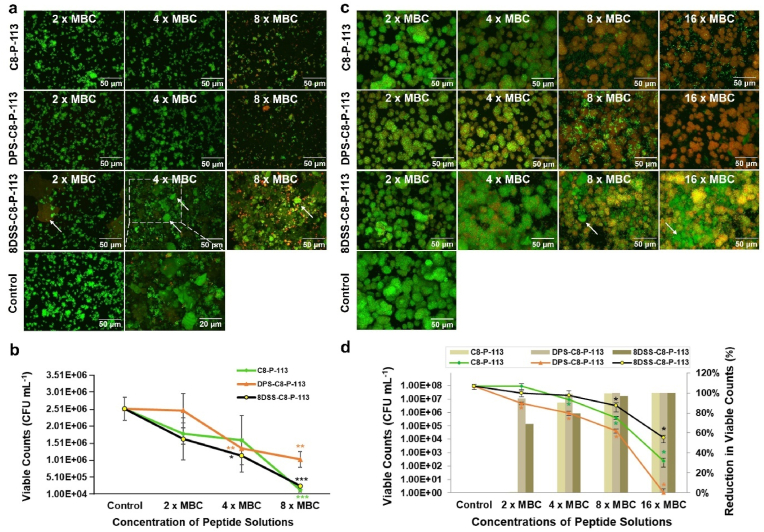
Fig. 1.
Anti-S. mutans adhesion and anti-S. mutans biofilm activity of peptide solution. (a) Fluorescence images ( × 60) of S. mutans adhesion on peptide-coated enamel surfaces in different groups with varied concentrations. (b) Viable counts of S. mutans adhesion on peptide-coated enamel surfaces after 5 h of incubation. (c) Fluorescence images ( × 60) of S. mutans biofilms in peptide solutions with different concentrations. (d) Viable counts (left: ordinate and point plot) and percentage reduction in viable counts (right: ordinate and bar chart) of S. mutans biofilms after 24 h of exposure to peptide solutions with varied concentrations. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, compared with control group. 8DSS-C8-P-113 hydrogel peptide was stained green and indicated by arrows.