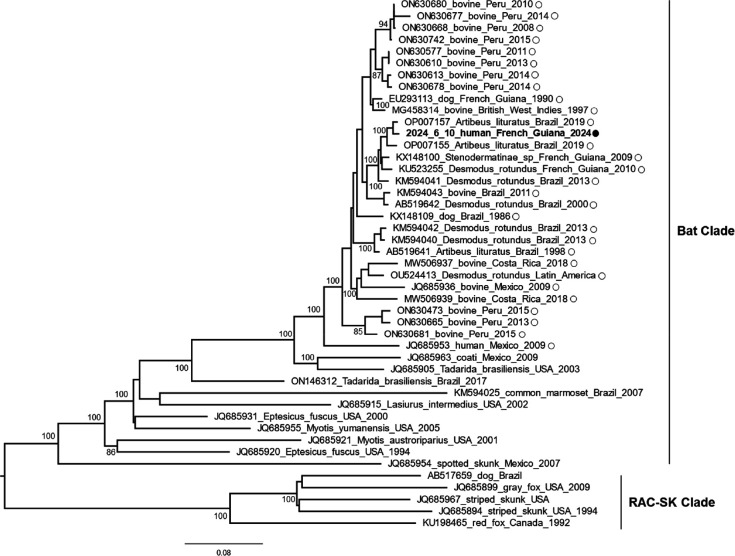
Fig 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the RABV strain (2024-6-10) obtained from the cerebellum of a deceased patient presenting with encephalitis of unknown etiology in French Guiana and different representative American strains. The tree was based on the multiple sequence alignment corresponding to the concatenation of the five ORFs (10,815–10,818 nt), performed with ClustalW (v2.1) (14) implemented in Galaxy@Pasteur (9). The tree was constructed using the ML approach based on the generalized time-reversible model proportion of invariable sites plus gamma-distributed rate heterogeneity (GTR+I+Γ4) utilizing Subtree Prune-and-Regraft (SPR) branch-swapping, as estimated in PhyML 3.0 (12) with Smart Model Selection, also implemented in Galaxy@Pasteur. The robustness of individual nodes was estimated using 100 bootstrap replicates. All tools were run with default parameters unless otherwise specified. The ML phylogenetic tree was visualized with FigTree (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/). Only bootstrap values ≥80 are indicated for the major branches. The scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. Each sequence denomination contains the GenBank accession number, the nature of the infected species, and the country and year of isolation, where applicable. Rabies virus isolates associated with vampire bats are indicated by an open circle. The isolate (2024_6_10_RABV_GUY) described in this study is indicated in bold, with a black circle. RAC-SK, raccoon–skunk (rabies virus associated with the raccoon and skunk host animals).