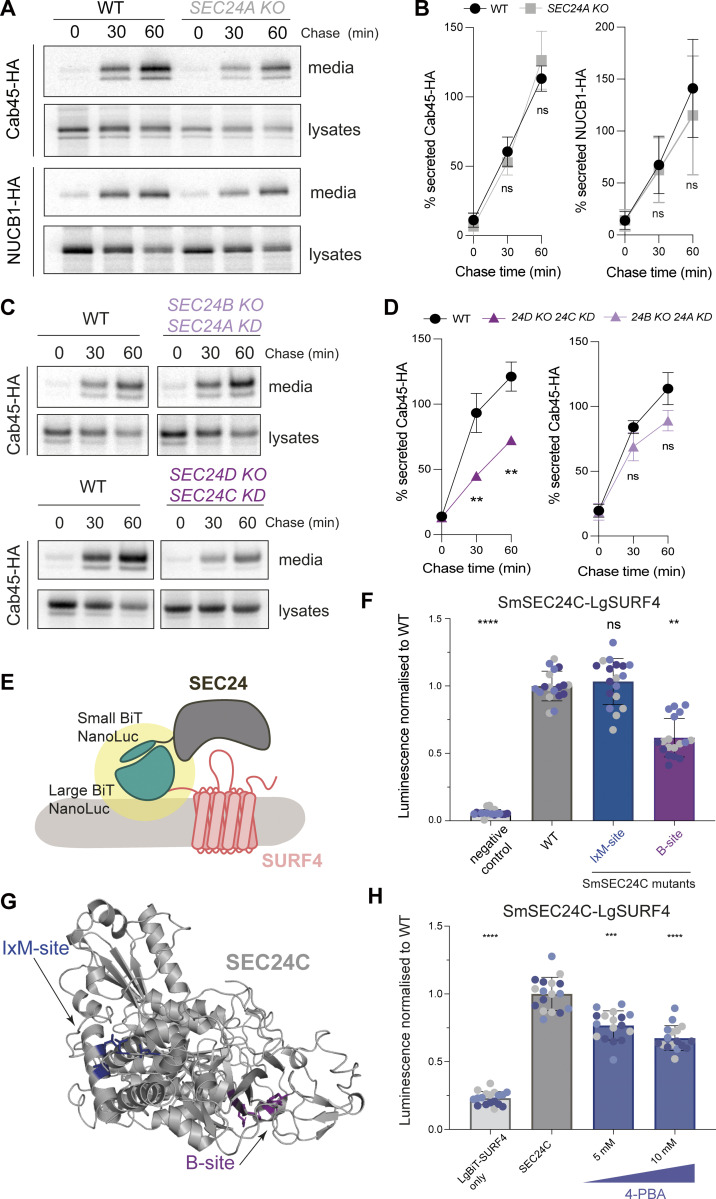
Figure 1.
SEC24C/D B-site drives Cab45 secretion. (A) Radiolabeled pulse-chase experiment testing Cab45 and NUCB1 secretion in WT and SEC24A KO cells. Transiently transfected HA-tagged proteins were immunoprecipitated from media and lysates at indicated time points after [35S]-Met/Cys addition and detected by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimage analysis. (B) Protein secretion shown in A was quantified from three independent experiments. (C) Radiolabeled pulse-chase experiment testing Cab45 secretion in WT and KO/KD cells as indicated. (D) Quantification of secretion experiments shown in B; n = 3. (E) Diagram of NanoBiT complementation assay to assess SURF4-SEC24 interactions. (F) NanoBiT luminescence measured upon co-expression of LgBiT-SURF4 with the indicated SmBiT-SEC24C mutants, normalized to WT values. Negative control was a smallBiT-PRKACA (activation of protein kinase A) fusion that controls for Small-BiT background complementation. (G) Crystal structure of SEC24C (PDB ID: 3EH2) showing the two binding sites tested in the NanoBiT assay. (H) NanoBiT luminescence was measured upon co-expression of LgBiT-SURF4 and SmBiT-SEC24C in the presence of the B-site-occluding small molecule, 4-PBA, normalized to WT. Negative control was largeBiT-PKAR2A (protein kinase cAMP-dependent type II regulatory subunit alpha) that controls for non-specific large-BiT binding. Six technical replicates were used in each of the three independent NanoBiT biological replicates, as indicated by differential coloring within superplots. Triangles represent mean and error bars represent SD. Statistical tests were one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction for multiple testing. Data distribution was assumed to be normal but this was not formally tested. ns = not significant. * = P value <0.033, ** = P value <0.002, *** = P value <0.0002, **** = P value <0.0001. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData F1.