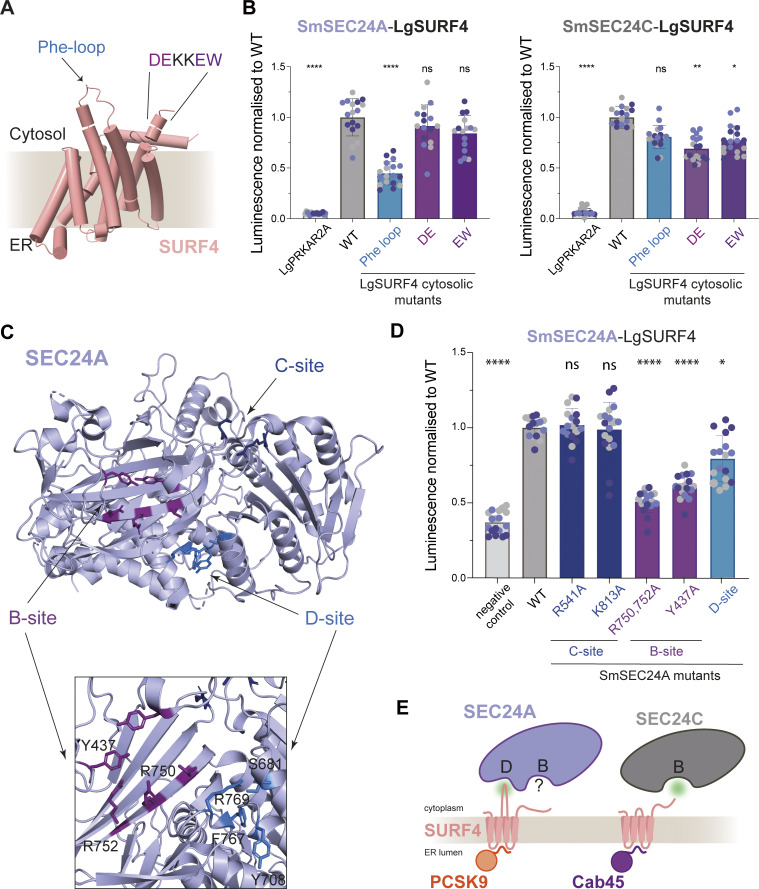
Figure 2.
Mutagenesis reveals complexity of SURF4 interactions with SEC24 paralogs. (A) AlphaFold2 model of SURF4, highlighting cytosolic regions important for SURF4-dependent cargo secretion identified by mutagenesis. (B) Luminescence values were measured upon co-expression of SmBiT-SEC24C or SmBiT-SEC24A with the indicated LgBiT-SURF4 mutants, normalized to WT values. (C) Crystal structure of SEC24A (PDB ID: 5VNO) showing the three binding sites tested in the NanoBiT assay; the neighboring B- and D-sites are zoomed in. (D) NanoBiT complementation measured upon co-expression of LgBiT-SURF4 and the indicated SmBiT-SEC24A mutants, normalized to WT. (E) Model summarizing secretion dissected by NanoBiT and pulse-chase. SEC24A engages SURF4 via a D-site-cytosolic loop interaction, whereas the B-site is important for PCSK9 secretion but not for SURF4 engagement. SEC24C engages C-terminal motifs of SURF4 via its B-site to drive Cab45 export. Statistical tests were one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s correction for multiple testing. Data distribution was assumed to be normal but this was not formally tested. ns = not significant, * = P value <0.033, ** = P value <0.002, *** = P value <0.0002, **** = P value <0.0001. For each NanoBiT experiment, six technical replicates were used in each of the three independent biological replicates, as indicated by differential coloring within superplots. Triangles represent mean and error bars represent SD.