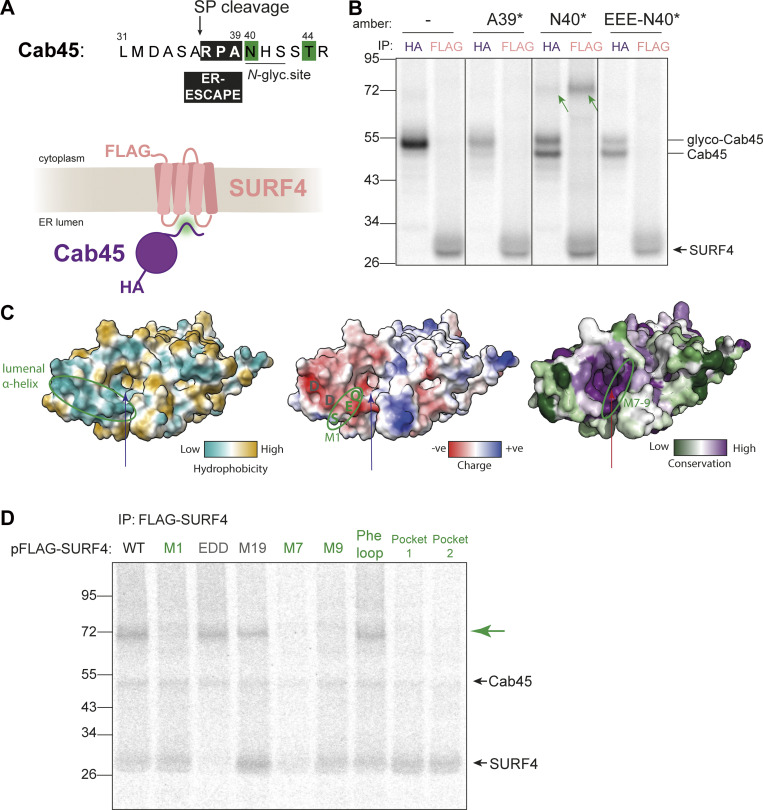
Figure 4.
ER-ESCAPE binds a conserved lumenal pocket of SURF4. (A) N-terminal amino acid sequence of Cab45. Numbering indicates amino acid positions from the N-terminus, including SP. An ER-ESCAPE motif (black box) follows a signal peptide cleavage site (arrow), followed by a putative N-glycosylation site. Green shading shows positions that were crosslinked to SURF4. (B) A site-specific photo-crosslinking experiment showing the dependence of Cab45-SURF4 interaction on ER-ESCAPE. HA and FLAG IPs were performed on UV-crosslinked semi-permeabilized cells. Green arrows indicate crosslinked species recovered by both Cab45-HA and FLAG-SURF4 IPs. Presumed migration of Cab45 species and SURF4 are indicated. (C) ER lumenal views of SURF4 AF2 structure predictions showing hydrophobicity, surface charge, and conservation scores (left to right). The long arrow points to the predicted pocket for ER-ESCAPE binding, the small arrow indicates another, smaller putative pocket. A lumenal α-helix previously shown to bind CW motifs, and M7-9 regions are circled. (D) IVT and site-specific photo-crosslinking of Cab45-N40* to SURF4 and its mutants. HEK-293TREx SURF4 KO cells were transfected with the indicated FLAG-SURF4 constructs 24 h prior to IVT. Further sample processing was performed as in B. SURF4 mutants in green are those that did not produce a cross-link with SURF4 (indicated by green arrow), and mutants in grey produced a crosslink. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData F4.