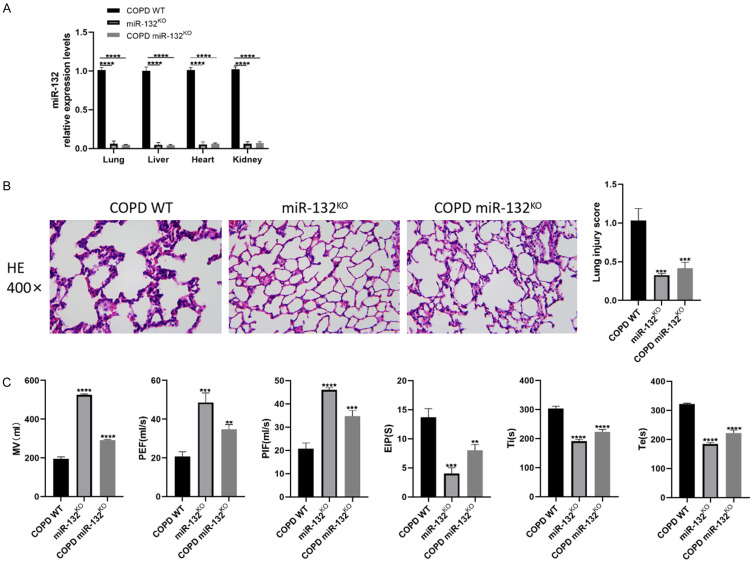
Figure 2.
The deletion of miR-132 improved pulmonary function of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) mice. miR-132KO mice and WT mice were administrated with CS exposure 2 hours per day for 8 weeks, n=8 per group. A. qRT-PCR analysis of miR-132 expression in the lung tissues, liver, heart, and kidney of miR-132KO mice and WT mice. B. H&E staining sections showing the lung injury in vivo (400×, scale bars =100 µm). C. Pulmonary function parameters including MV, PIF, PEF, EIP, Ti and Te were determined. Results are expressed as mean ± SD, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, vs COPD WT mice. Abbreviations: PIF: peak inspiratory flow; PEF: peak expiratory flow; EIP: end-inspiratory phase; MV: minute ventilation; Ti: inspiratory duration; Te: expiratory duration; SD: Standard Deviation; CS: smoking cigarettes; COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; WT: wild type; p: p value.