Fig. 4|. Bile acid biotransformations in the human large intestine.
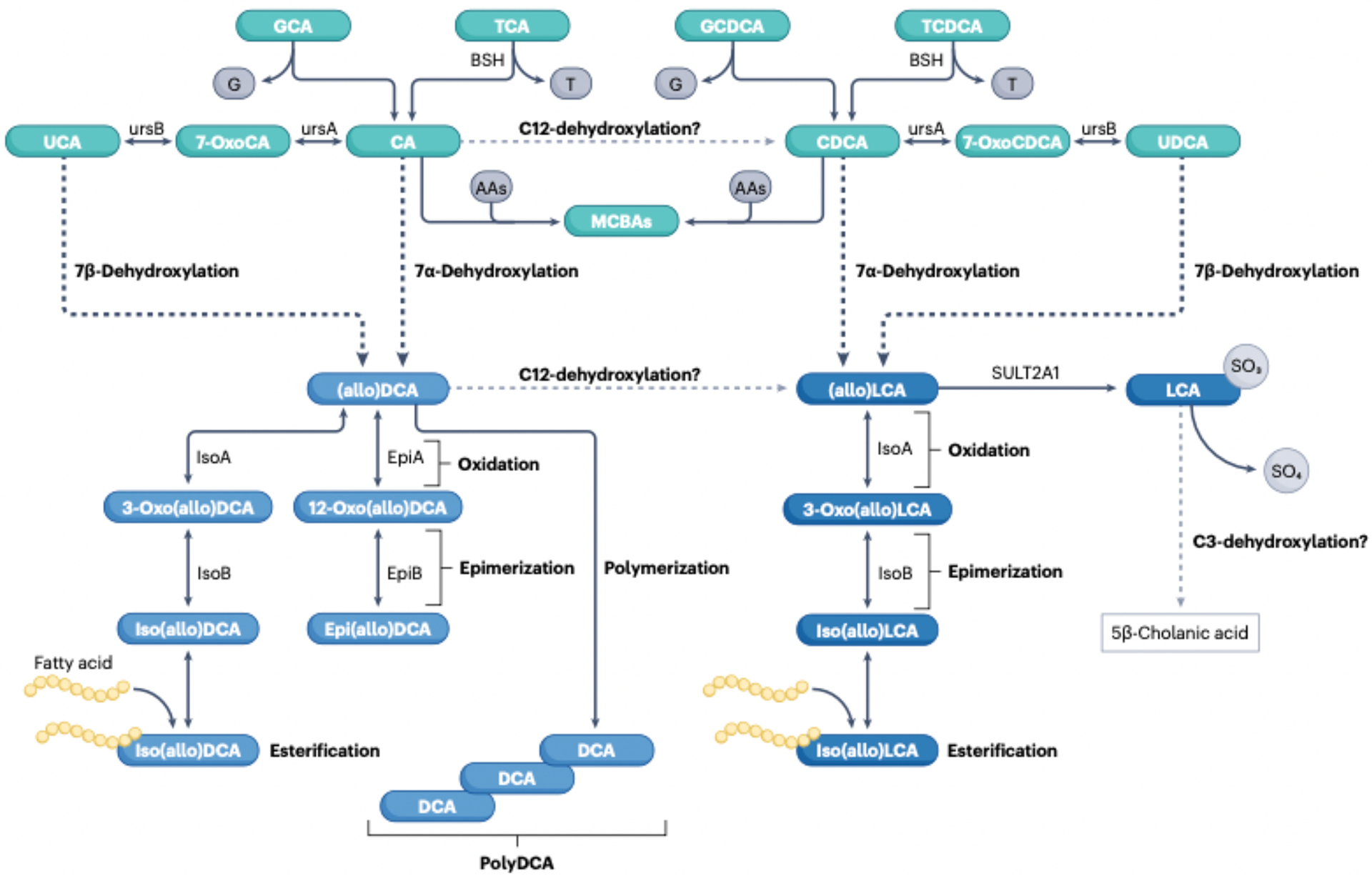
Conjugated primary bile acids (taurocholic acid (TCA), glycocholic acid (GCA), taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA), glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA)) enter the large intestineand are deconjugated by the enzyme bile salt hydrolase (BSID by diverse gut bacterial taxa (Table 1). BSH is also reported to reconjugate free bile acids with a wide range of amino acids (AAs) yielding microbially conjugated bile acids (MCBAs). The primary bile acids cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid i.CDCA) can be oxidized to 7-oxoCA and 7-oxoCDCA, respectively, by the enzyme 7α hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase(ursA) (Table 1) and epimerized to ursochollc acid (UCA) and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), respectively, by the enzyme 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase(ursB). CA and CDCA are also converted to deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), respectively, through the multipstep Hylemon-Björkhem pathway of bile acid 7α-dehydroxylation by intestinal Clostridia (Table 1). UCA and UDCA can be directly 7β-dehydroxylated through the Hylemon-Björkhem pathway or, alternatively, epimerized back to CA and CDCA and 7α-dehydroxylated to DCA and LCA. The Hylemon-Björkhem pathway also yields A/B-ring epimers that are planar, known as ‘allo’ bile acids. We have designated both epimers of DCA and alloDCAas (allo)DCA as well as (allo)LCA and their derivatives. (allo)DCA has two hydroxyl groups that can be oxidized to 3-oxoDCA by 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (isoA) and/or 12-oxoDCA by 12ahydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (epiA), and epimerized by 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (isoB) and/or 12β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (epiB) to iso(allo)DCA and epi(allo)DCA, respectively. (allo)LCA is monohydroxylated at C3 and can yield 3-oxo(allo)LCA and lso(allo)LCAonly. Additionally, the host sulfates lca to yield 3-sulfoLCA. It is reported that 3 sulfoLCA can be C3-dehydroxylated to the non bile acid, 5β-cholanic acid. isoDCA and isoLCA are also esterified to short-chain and long-chain fatty acids.and DCA can be polymerized through esterification between C3-OH and C24-COOH. There is some support for the C12-dehydroxylation of CA to CDCA and of DCA to LCA.
