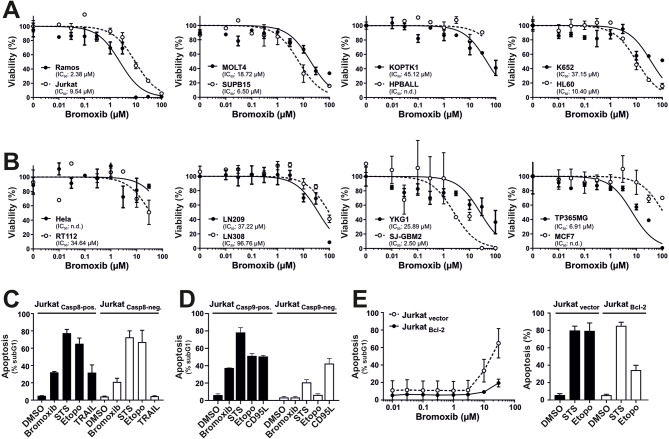
Fig. 2.
Bromoxib exhibits cytotoxic effects in various cancer cell lines and triggers apoptosis through the intrinsic mitochondria-dependent pathway. Cytotoxicity was determined after 24 h with increasing concentrations of bromoxib in various human cancer cell lines: (A) Leukemia and lymphoma cell lines: HL60 (acute myeloid leukemia; AML), HPBALL (T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; T-ALL), Jurkat (T-ALL), KOPTK (T-ALL), MOLT4 (T-ALL), SUPB15 (B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; B-ALL), K652 (chronic myeloid leukemia; CML), Ramos (Burkitt B cell lymphoma), and (B) solid tumor cell lines: HeLa (cervical cancer), MCF7 (breast cancer), RT112 (bladder cancer), LN209, LN308, YKG1, SJ-GBM2, and TP365MG (different glioblastoma cell lines). Cell viability was assessed by AlamarBlue® viability assay. Shown in each graph is the mean ± SD of one representative experiment performed in triplicates. The respective IC50 values are shown within the graphs. n.d.=not determinable in the depicted concentration range. (C) Bromoxib induces caspase 8 independent and (D) caspase 9 dependent apoptosis. After incubating for 24 h, apoptosis-related DNA degradation was observed by measuring propidium iodide-stained apoptotic hypodiploid nuclei using flow cytometry in (C) caspase 8-positive and caspase 8-negative Jurkat cells and (D) caspase 9-positive and caspase 9-negative Jurkat cells. Cells were stimulated with bromoxib (10 µM), staurosporine (STS; 2.5 µM), etoposide (Etopo; 50 µM), and DMSO (0.1% v/v; diluent control). For stimulation of death receptors in (C) TRAIL (Tumor Necrosis Factor Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand; 40 ng/ml) or (D) CD95-ligand (CD95L) (500 ng/ml) were applied. Error bars = mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed in triplicates. (E) Bromoxib-induced apoptosis is blocked in the presence of antiapoptotic Bcl-2. Apoptosis induction was analyzed in Jurkat cells stably transfected with vectors encoding Bcl-2 or empty vector. After 24 h apoptosis induction was assessed by propidium iodide staining of apoptotic nuclei and flow-cytometry. Cells were treated with different concentrations of bromoxib (left panel) and respective controls, STS (2.5 µM), Etopo (50 µM), and DMSO (0.1% v/v) (right panel). Error bars = mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed in triplicates