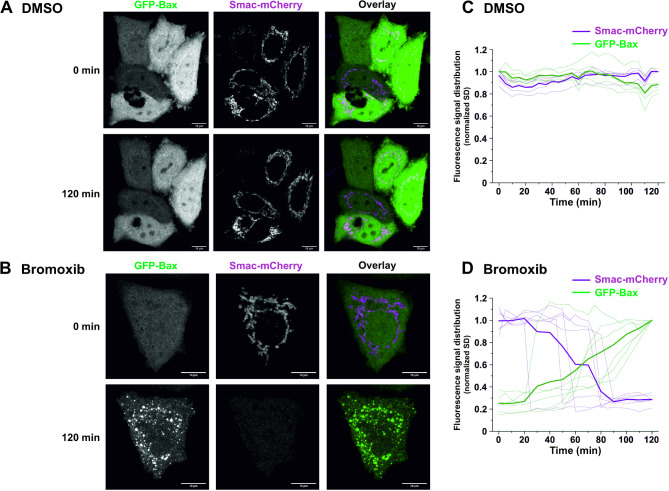
Fig. 3.
Bromoxib triggers the recruitment of Bax to the mitochondria and the mitochondrial release of the proapoptotic protein Smac. (A) and (B) confocal live cell imaging of HeLa wild type cells expressing GFP-Bax (green) and Smac-mCherry (magenta) upon treatment with (A) DMSO (0.1% v/v,) or (B) bromoxib (10 µM). HeLa cells were intentionally used to better track the localization of GFP-Bax and Smac-mCherry. To exclude downstream caspase-mediated effects on cell morphology (such as membrane blebbing), 10 µM of the caspase-inhibitor QVD was added prior to incubation with DMSO or bromoxib. Scale bars indicate 10 μm. (C) and (D) quantification of the effects of bromoxib on mitochondrial Bax accumulation and Smac release in HeLa wild type cells. The normalized standard deviation (SD) of the fluorescence intensity of GFP-Bax and Smac-mCherry upon treatment with (C) DMSO or (D) bromoxib was used as a measure of subcellular distribution, in individual cells (n = 5–6) from 3 independent experiments. Thinner lines represent measurements of individual cells, while thicker lines represent the average of all recorded cells. A low SD corresponds to homogenous distribution, while a high SD corresponds to an accumulation