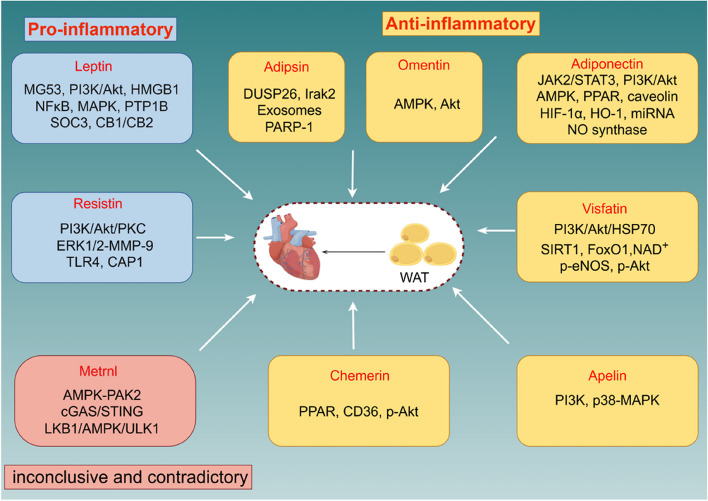
Fig. 2.
The function and main molecular mechanism of various adipokines on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Adipokines are mainly divided into two categories: anti-inflammatory (including adiponectin, adipsin, visfatin, chemerin, omentin and apelin, related signaling pathways are marked in each corresponding yellow box) and pro-inflammatory (leptin and resistin, related signaling pathways are marked in each corresponding blue box), while metrnl (related signaling pathway are marked in red box) exhibit opposite effects in various pathological condition. WAT: white adipose tissue; JAK2: janus-activated kinase 2; STAT3: signal transducers and activators of transcription 3; PI3K:phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt: protein kinase B; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; miRNA: microRNA; NO synthase: nitric oxide synthase; HSP70: heat shock protein 70; SIRT1: sirtuin 1; FoxO1: the class O of Forkhead box 1; NAD.+: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; p-eNOS: phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase; p-Akt: phosphorylation of protein kinase B; p38/MAPK: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; CD36: cluster of differentiation 36; PAK2: serine/threonine protein kinase 2; cGAS-STING: Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase-Stimulator of interferon genes; LKB1: Liver Kinase B1; ULK1: UNC-51LikeAutophagyAckingKinase1; PKC: protein kinase C; ERK 1: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1; ERK2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2; MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; CAP1: adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1; MG53: mitsugumin 53; HMGB1: high mobility group box1protein; NFκB: Nuclear Factor kappa B; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; PTP1B: protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; SOC3: suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; CB1: Cannabinoid Receptor 1; CB2: Cannabinoid Receptor 2