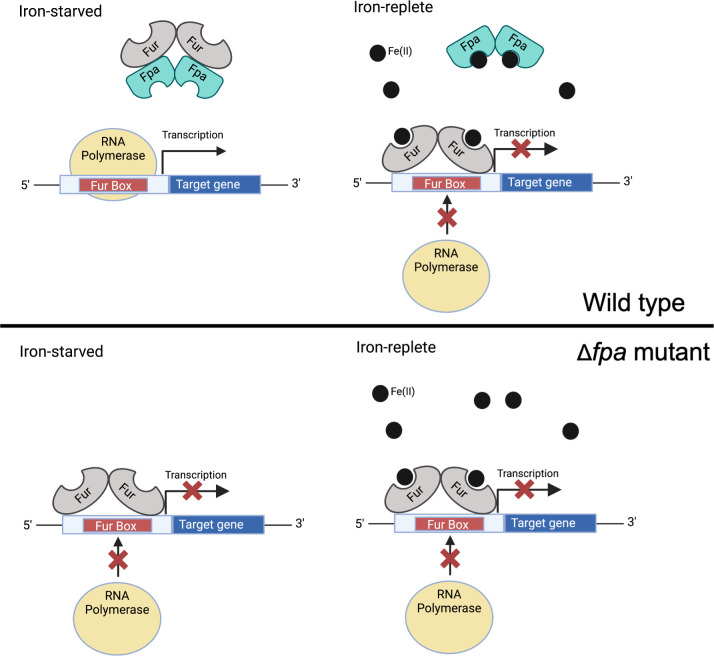
Fig 8.
Working model for Fpa function. In our model, Fur (gray) and Fpa (cyan) bind Fe(II) transiently. They are both metalated in Fe-replete growth conditions, and Fur directly prevents transcription of genes coding for Fe acquisition machinery via binding to a consensus sequence of DNA in the operator termed a Fur box. Upon Fe limitation, Fpa forms a complex with Fur preventing Fur from binding to Fur box DNA, thus alleviating Fur repression of target genes. The oligomeric state of the heterocomplex is currently unknown.