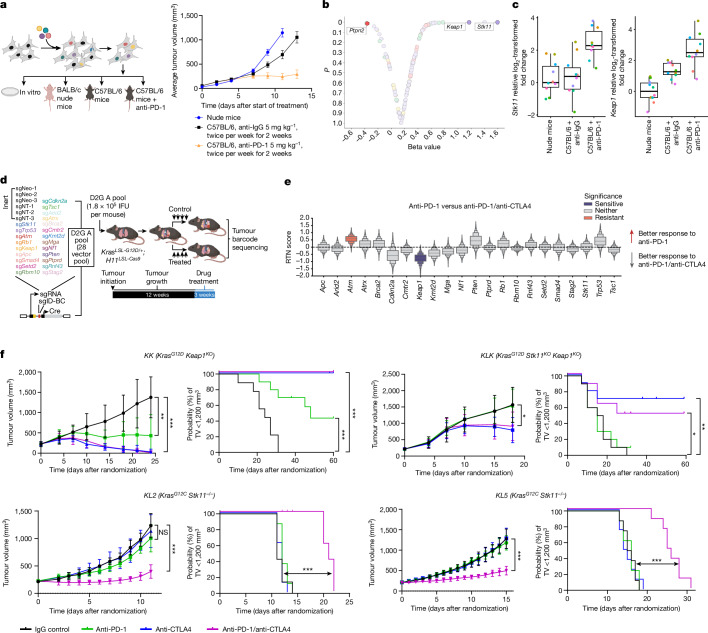
Fig. 3. Efficacy of anti-PD-1 monotherapy and dual anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA4 therapy in immune-competent models of STK11- and/or KEAP1-deficient NSCLC.
a, Left, in vivo TSG-focused CRISPR–Cas9 screening platform for identifying drivers of PD-1 inhibitor resistance. Right, the gradual decrease in tumour growth from untreated nude mice (n = 18) to C57BL/6 mice treated with anti-IgG (n = 18) to C57BL/6 mice treated with anti-PD-1 (n = 20) reflects increased anti-tumour immunity. Data are mean ± s.e.m. b, Volcano plot of relative sgRNA enrichment or depletion in tumours from C57BL/6 mice that were treated with anti-PD-1 (5 mg per kg; n = 20; 10 mg per kg; n = 25; total n = 45) versus anti-IgG isotype control (n = 18). c, Box plots of relative log2-transformed fold change for sgRNAs targeting Stk11 (left) or Keap1 (right) across treatment groups (nude, n = 18; IgG, n = 20; anti-PD-1 5 mg per kg, n = 20). Individual sgRNAs are represented by coloured circles (10 sgRNAs per gene). Median (central line), interquartile range (box plot edges) and data range (whiskers) are indicated. d, PGx-Tuba-seq experimental strategy for in vivo multiplexed quantitative evaluation of the effect of TSG depletion on immunotherapy responses in an autochthonous, genetically engineered KrasG12D-driven LUAD model (see Methods). IFU, infectious units. e, Relative tumour number (RTN) score reflecting differential sensitivity to dual anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA4 blockade compared with anti-PD-1 monotherapy. Significant effects are highlighted in colour (n = 16–19 mice per group). f, Sensitivity to dual ICB across several STK11 and/or KEAP1-deficient syngeneic models of KrasG12D (KK, KLK) and KrasG12C (KL2, KL5) mutant NSCLC (n = 8–10 mice per group). Comparison of tumour volume (TV) was performed at the time point at which the first mouse in any treatment arm reached end-point (tumour volume ≥ 1,500 mm3) and was based on the Mann–Whitney U test. Data are mean ± s.d. Time to tumour volume (TTV) ≥ 1,200 mm3 was used as a surrogate for survival. Comparison of TTV between treatment groups was based on the log-rank test. Statistical significance is indicated (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001).