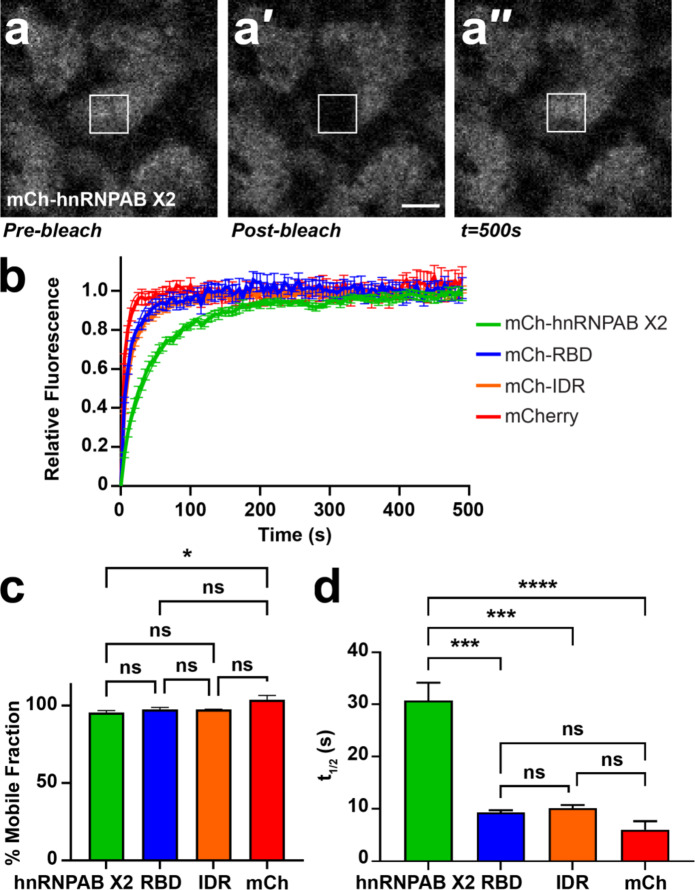
Fig. 4.
hnRNPAB X2 dynamically associates with L-bodies via its RBD and IDR. (a) Shown is an image of the vegetal cytoplasm of a stage II oocyte expressing mCh-hnRNPAB X2. FRAP was conducted such that an individual L-body was partially bleached (a′), to allow for recovery (a′′) both from within the L-body and from its environment. The 10 μm2 ROI is indicated by a white box; scale bar = 10 μm. (b) Stage II oocytes were microinjected with mCherry (mCh), mCh-hnRNPAB X2, mCh-RBD or mCh-IDR RNA to express the mCh-tagged proteins, along with Cy5 LE RNA to mark L-bodies. Normalized FRAP recovery curves are shown (n = 21 oocytes per fusion protein); error bars represent standard error of the mean. Measurements were taken at 5 s intervals over 100 iterations. (c) Plateau values (% mobile fraction) are shown for mCh-hnRNPAB X2 (green, 96%±0.013), mCh-RBD (blue, 98%±0.014), mCh-IDR (orange, 98%±0.002), and mCherry (red, 104%±0.29). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Statistics shown are an Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons; ns indicates not significant (p > 0.05) and * indicates p = 0.04. (d) T1/2 measurements are shown for mCh-hnRNPAB X2 (green, 30.1s ± 3.4), mCh-RBD (blue, 9.3s ± 0.4), mCh-IDR (orange, 10.1s ± 0.6), and mCherry (red, 6.0s ± 1.6), measured as the average time at which the protein recovers half of its plateau value. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Statistics shown are an Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons; ns indicates not significant (p > 0.05), *** indicates p < 0.001, **** indicates p < 0.0001.