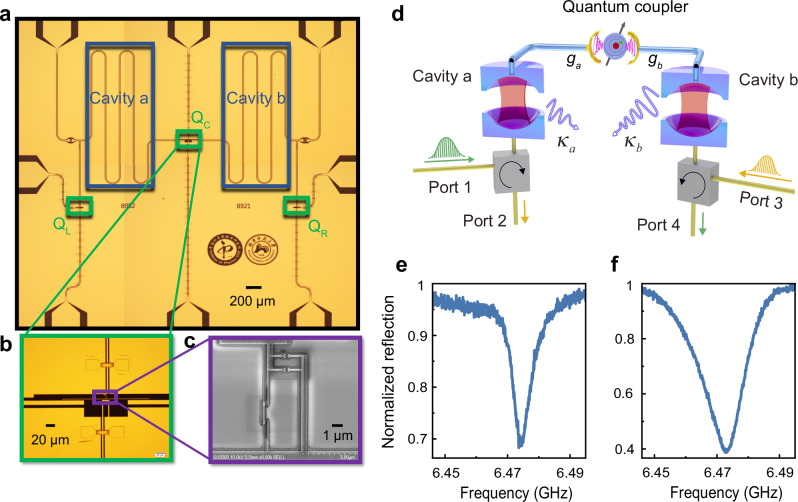
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the superconducting quantum chip.
a Optical micrograph of the coupling qubit and the two indirectly-coupled coplanar waveguide (CPW) cavities. Two CPW cavities have the same resonant frequency of GHz but different decay rates of MHz and MHz. There are three tunable-gap flux qubits. The left (right) qubit QL (QR) only couples to the left (right) CPW cavity and works as a cavity frequency shifter to tune the resonant frequency of the left (right) cavity. The central qubit QC couples to the two cavities as a quantum coupler to tune the coupling strength between the two cavities. Optical micrograph (b) and scanning electron micrograph (c) of the coupling flux qubit. d Equivalent schematic diagram in which two cavities couple with each other by a quantum coupler. Each cavity is connected to a circulator for extending ports. Reflection spectra of the left high-Q cavity (e) and the right low-Q cavity (f) that display Lorentzian lineshapes detected at low probing power to keep the average photon numbers inside the cavities less than one.