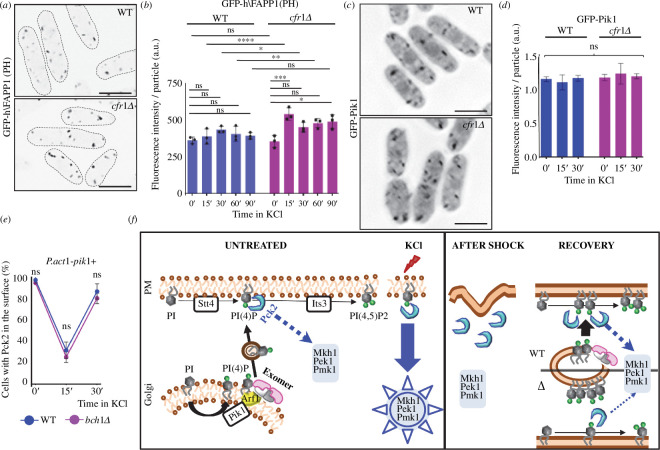
Figure 6.
Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P) homeostasis in the Golgi is altered in exomer mutants undergoing osmotic stress. ( a ) Micrographs of cells from the wild-type control (WT) and cfr1Δ strains bearing the GFP-h\FAPP1(PH) probe, which binds PI4P in the Golgi. The cells were treated with 0.6 M of KCl for 15 min . The images were captured with a Dragonfly spinning disk microscope and are average (AVG) projections. ( b ) The GFP fluorescence was quantified from photographs of the strains used in ( a ) treated with 0.6 M of KCl for the indicated times (minutes). ( c ) Micrographs of WT and cfr1Δ cells bearing GFP-Pik1. The images are AVG projections captured with a DeltaVision. ( d ) The GFP fluorescence was quantified from photographs of the strains used in ( c ) , treated with 0.6 M of KCl for the indicated times (minutes). ( e ) Control (WT) and bch1Δ cells that bear Pck2-GFP and express pik1+ from the P.act1+ promoter were treated with 0.6 M of KCl for the indicated times (minutes), and photographed. The percentage of cells exhibiting fluorescence in the cell poles and cell sides, but not in the cell equator and septa ( Materials and methods) were scored from the images. ( f ) Speculative model to explain the role of exomer in PI4P homeostasis and CIP regulation. Left panel, under basal conditions (UNTREATED), the 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Stt4 phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol (PI) and generates PI4P in the plasma membrane (PM). This PI4P is the substrate for the 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase Its3 that produces phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2]. Pck2 binds to the PI4P and activates the CIP MAP kinase in response to stress (KCl). In the Golgi, 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase Pik1 phosphorylates PI to generate PI4P. Exomer, which interacts with Arf1 and the Golgi membrane, would modulate the transfer of PI4P to the PM. Right panel, osmotic shock would alter the properties of the PM, and Pck2 would dissociate from the surface of cell poles (AFTER SHOCK). After the initial shock, the WT cells (WT) would adapt to the presence of KCl (RECOVERY); Its3 would synthesize PI(4,5)P2 from the PI4P generated in the PM by Stt4. Under these conditions, there would be enhanced transport of PI4P from the Golgi to the PM that would mediate Pck2 re-association with the PM. In the absence of exomer (Δ), this transport would be inefficient, which would result in PI4P accumulation in the Golgi, shortage of this lipid in the PM, and reduced Pck2 association with the PM and CIP signalling. In ( a ) and ( c ), scale bar, 10 µm. In ( b ) and ( d ), a.u., arbitrary units. In ( b ), ( d ) and ( e ), the Šidák correction was used after ANOVA to determine the statistical significance of the differences. ns, non-significant; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.