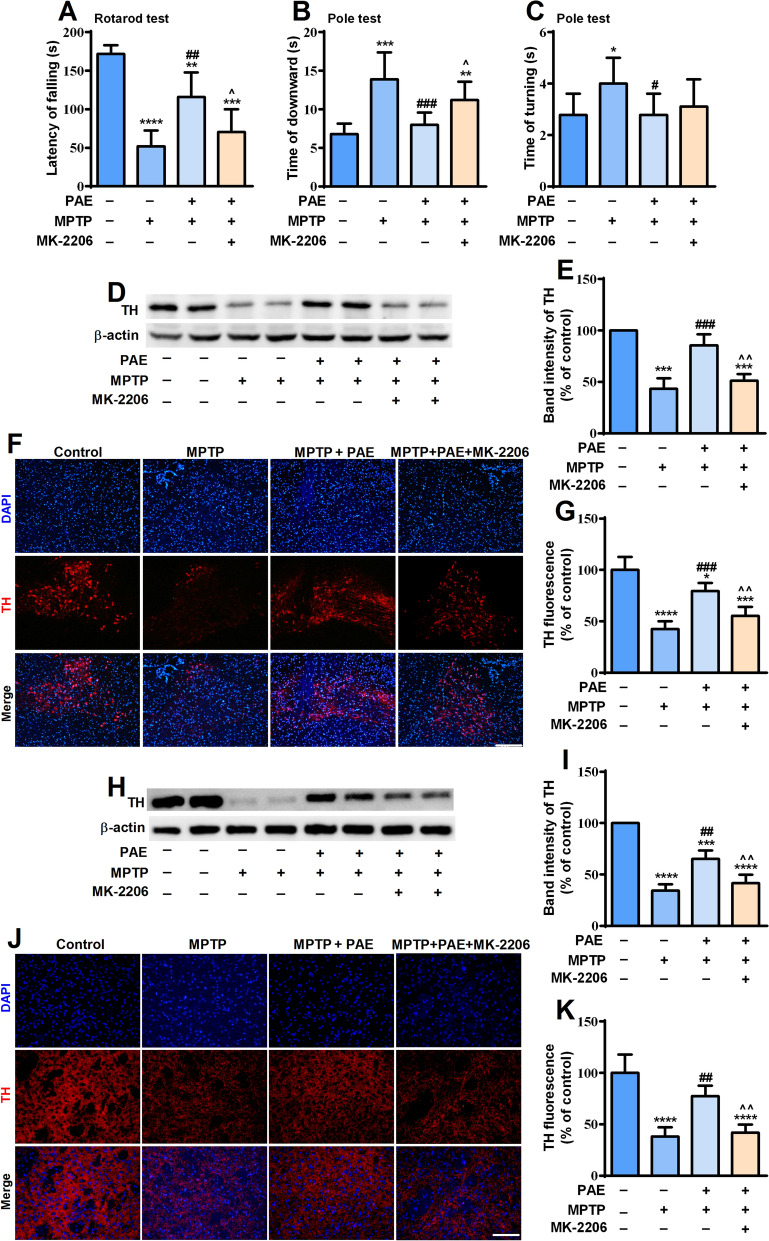
Fig. 9.
PAE improves the behavioral deficits and inhibits the loss of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra and striatum of MPTP-treated mice through AKT pathway. A The performance of mice in Rotarod test. PAE administration increased the time of MPTP-treated mice staying on the rod, while MK-2206 blocked the effect of PAE (n = 8). B The graph showed the time that the mice took to climb down the pole. PAE reduced the time of MPTP-treated mice took to climb down the pole, MK-2206 attenuated the effect of PAE (n = 8). C The graph showed the time that the mice took to turn around in the pole test (n = 8). The representative western-blot analysis of TH expression in the substantia nigra (D) and striatum (H). PAE treatment inhibited the down-regulation of TH in substantia nigra and striatum caused by MPTP, MK-2206 blocked the effect of PAE (E, I). PAE prevented the loss of TH-positive neurons in the substantia nigra (F, G) and TH-positive fiber density in striatum (J, K) determined by immunofluorescence staining, MK-2206 blocked the effect of PAE, bar = 200 μm, n = 3. Data are presented as mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, vs. control group, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, vs. MPTP group, ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01, vs. MPTP + PAE group