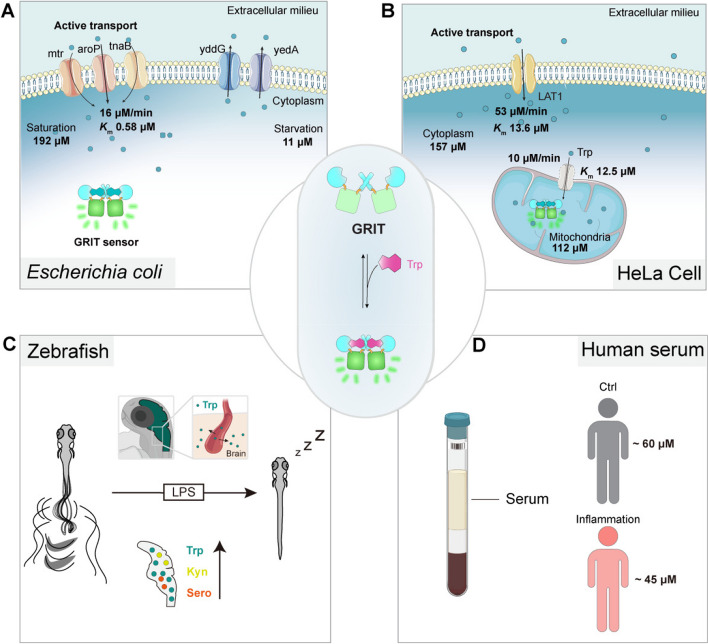
Fig. 5.
The proposed biophysical models of tryptophan dynamics in bacteria, mammalian cells, zebrafish, and human serum. A Pathways contributing to tryptophan metabolism in bacteria. Bacteria absorb external tryptophan mainly by aroP and export excess tryptophan with yddG and yedA. Gut microbe could utilize tryptophan to synthesize indole compounds to regulate neuron activities. B Proposed model for the tryptophan metabolism in the mitochondria of mammalian cells. Tryptophan enters mitochondria as the speed of 10 μM/min. Mitochondrial tryptophan pool depends on the cytosolic influx and endogenous consumption. C Proposed model of tryptophan dynamics in zebrafish larvae under LPS-induced inflammation. During inflammation, plasma tryptophan enters the brain and increases the levels of kynurenine and serotonin, leading to prolonged sleep time of zebrafish larvae. D The serum tryptophan levels in inflamed patients and control individuals. All the uptake rates or efflux rates are calculated at the Trp concentration around the Michaelis constant (Km) of relative transporters