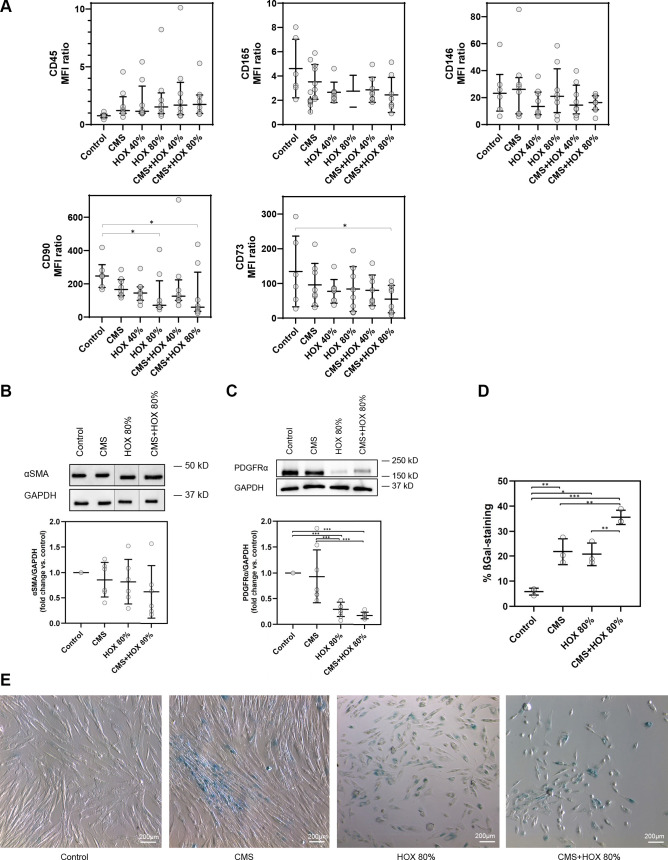
Figure 2.
Surface and intracellular alterations in lung resident mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) induced by cyclic mechanical stretch (CMS) and hyperoxia (HOX). A: hyperoxic exposure (HOX 80%) and/or CMS plus HOX 80% reduced the expression of CD73 and CD90 surface marker expression. MFI ratio log10 (specific stain/control). B and C: intracellular phenotype alterations in lung resident MSC of preterm infants after exposure to cyclic mechanical stretch (CMS) and/or hyperoxia (HOX). B: Western blot analysis showed no significant change in α-SMA expression after selective and combined treatment with CMS and HOX 80% for 72 h. n = 6 different MSC cultures. The order of samples was rearranged for the clearness of presentation without any further manipulation (indicated by separated boxes). The bar graphs show the densitometry results expressed as the ratio of adjusted total band volume normalized to GAPDH and control. C: level of PDGFRα was reduced by CMS and HOX 80% whereby HOX 80% and HOX 80% plus CMS demonstrated the largest effect size after 72 h treatment. n = 8 different MSC cultures. The bar graphs show the densitometry results expressed as the ratio of adjusted total band volume normalized to GAPDH and control. D and E: CMS and/or HOX 80% increased cellular senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA β-Gal) activity (blue; bright-field microscopy) after 72 h of exposure. Representative experiment of n = 3. Bar graph shows mean percentage of β-Gal positive cells of all experiments. Data are expressed as means (or median) ± SD (or IQR), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, by one-way RM ANOVA and Bonferroni-correction.