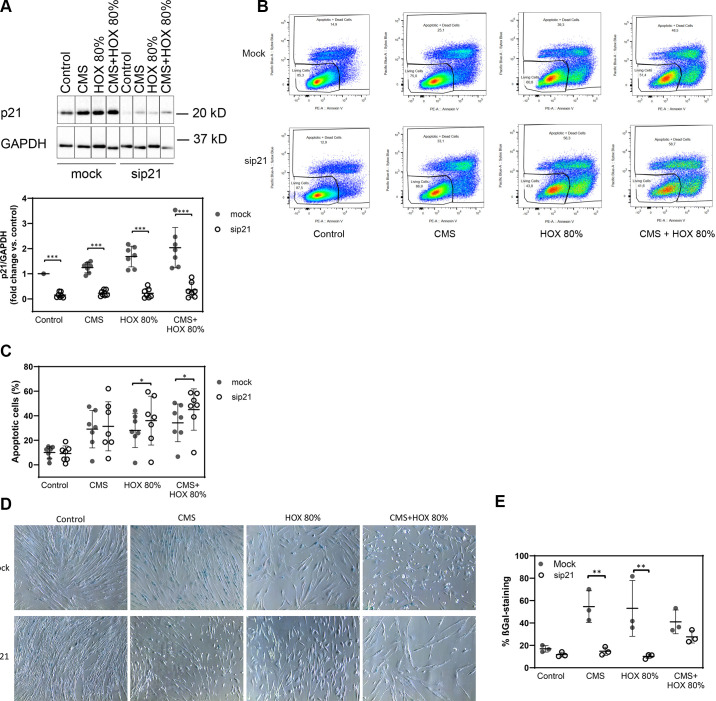
Figure 6.
Inhibition of p21 augments apoptosis induction by cyclic mechanical stretch (CMS) and hyperoxia (HOX) in lung resident mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) of preterm infants. A: representative Western blot analysis of sip21 transfected cells shows inhibited accumulation. n = 7 samples. The order of samples was rearranged for the clearness of presentation without any further manipulation (indicated by separated boxes). The bar graphs show the densitometry results expressed as the ratio of adjusted total band volume normalized to GAPDH and control. B: representative flow cytometry analysis of each intervention group shows increase of apoptotic cell fraction in sip21 transfected MSC for each treatment with CMS and/or HOX 80%. Live/dead staining via Annexin V/SYTOX Blue flow cytometry analysis, absolute cell death (%) = dead cells/frequency of single cells. C: inhibition of p21 augments apoptosis induction by CMS and HOX. When MSC with silenced p21 were exposed to CMS and/or HOX 80%, apoptosis induction was significantly increased and the increase in cell death was most pronounced for the combined intervention group. n = 7 samples. D and E: fraction of cells with induction of cellular senescence was reduced in MSC with silenced p21. One representative out of three experiments (blue; bright-field microscopy) Bar graph shows mean percentage of β-Gal positive cells of all experiments. Data are expressed as means ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by paired t test.