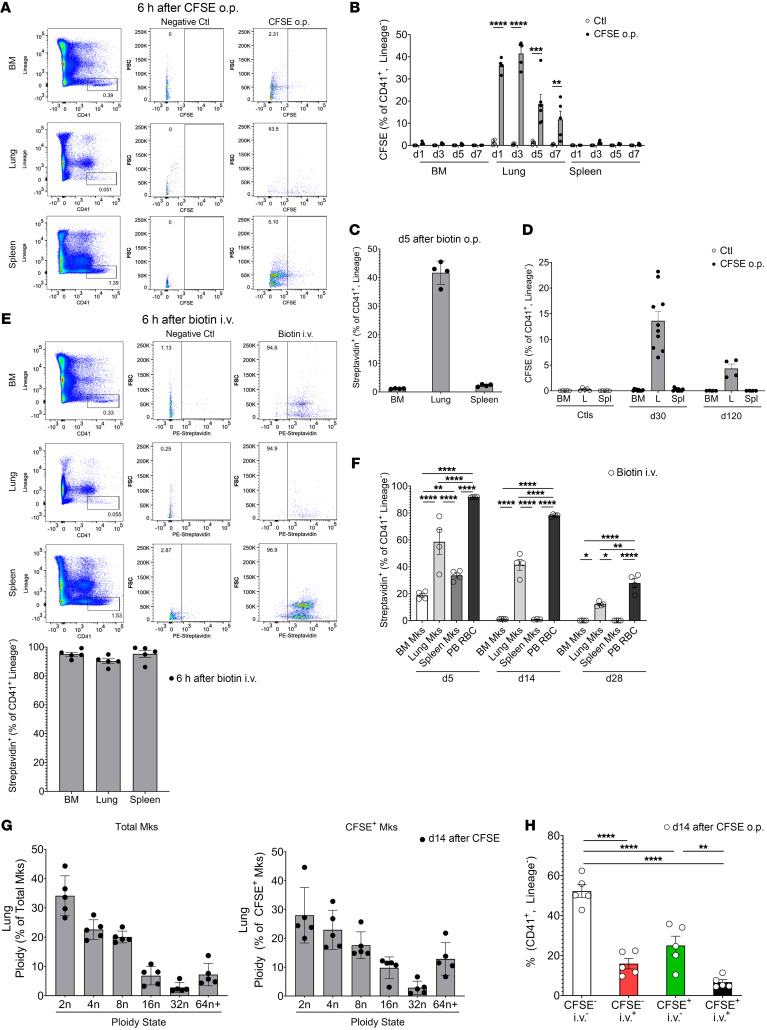
Figure 1. Lung Mks are long-lived cells.
(A and B) CFSE or (C) biotin was delivered o.p. to mice and showed specific labeling of lung Mks, but not BM or splenic Mks. (A) CFSE 6 hours later (n = 4, 2 independent experiments), (B) CFSE on day 1 (d1) to day 7 (d7) (n = 4–5 per group from 2 independent experiments) and (C) on day 5 after biotin o.p. labeling (n = 4; results are representative of 2 independent experiments). (D) CFSE-labeled lung Mks were present up to 120 days after CFSE administration (n = 10 from 2 independent experiments for day 30; n = 4 for day 120 from 1 independent experiment). L, lung; Spl, spleen. (E) Representative flow cytometry and quantitation results 6 hours after biotin i.v. labeling of BM, splenic, and lung Mks, similar to A (n = 4; results are representative of 2 independent experiments). (F) Biotin-labeled lung but not BM or splenic Mks were present up to 28 days following i.v. delivery (n = 4; results are representative of 2 independent experiments). RBCs were used as a positive control. PB, peripheral blood. (G) Total lung Mks and CFSE+ Mks had similar ploidy (day 14 after CFSE) (n = 5, representative results are from 2 independent experiments). (H) CFSE– and CFSE+ lung Mks had a similar intravascular (CD42d+) and extravascular (CD42d–) distribution (CD42d given i.v.) (n = 5; results are representative of 2 independent experiments). Data indicate the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, by (B) multiple t tests with Holm-Šidák multiple-comparison correction, (D and F) 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison correction, and (H) 1-way ANOVA with Šidák multiple-comparison correction. Ctl, control; FSC, forward scatter.