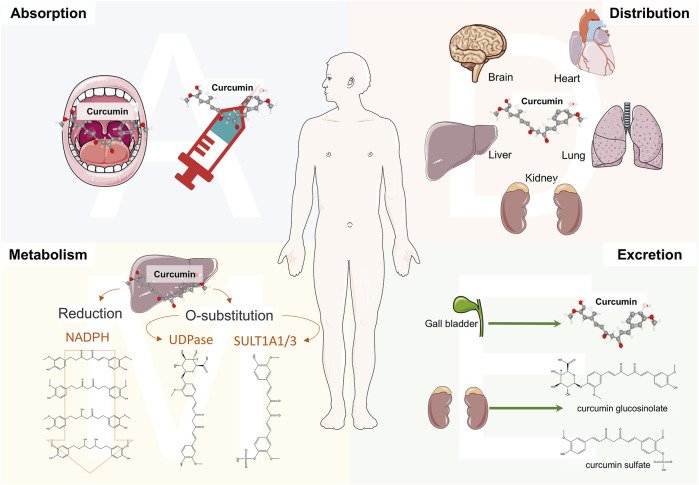
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in vivo. The administration methods of curcumin (CU) include oral and the injection of the vein and abdominal cavity. CU entering the body is mainly distributed in the liver, kidneys, brain, and lungs. Particularly, CU could cross the blood-brain barrier in the brain, which is the basis for treating neurological disorders. The liver is the main metabolizing organ for curcumin and can generate a range of metabolites such as CU glucosinolates, CU sulfates, and hydrogenated curcuminoids by O-substitution and reduction pathways. Renal excretion is the metabolic pathway for CU glucosinolate and CU sulfate. Meanwhile, CU can be excreted through bile.