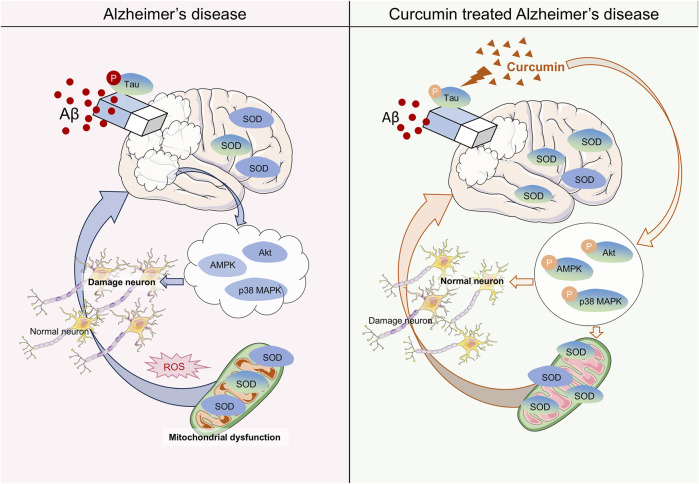
FIGURE 2.
Mechanisms of Curcumin in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). The mechanism of AD by affecting oxidative stress with Curcumin (CU). Curcumin reduces the AB and the hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins in the brain. In neuronal cells, curcumin increases the activity of the SOD enzyme to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction caused by oxidative stress. Meanwhile, CU improved the phosphorylation process of the AKT/p38 MAPK pathway to reverse neuronal apoptosis caused by oxidative stress.