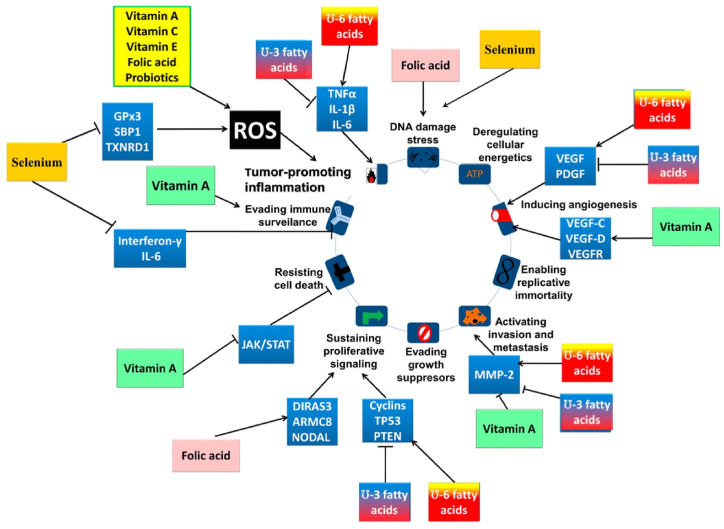
Fig. 2.
Nutrients impact cancer through their influence on molecular targets associated with cancer hallmarks, primarily by modulating the production of ROS, which play a crucial role in tumor-promoting inflammation. Beyond this, nutrients affect various cancer hallmarks; for instance, fatty acids influence tumor-promoting inflammation, promote angiogenesis, activate invasion and metastasis, and sustain proliferative signaling. These effects significantly alter an individual's susceptibility to cancer and their prognosis. By tailoring dietary interventions, it's possible to develop personalized nutrition strategies that specifically address these aspects, potentially improving cancer outcomes. The figure has been reproduced with the permission from Ref. [6]. Copyright 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.