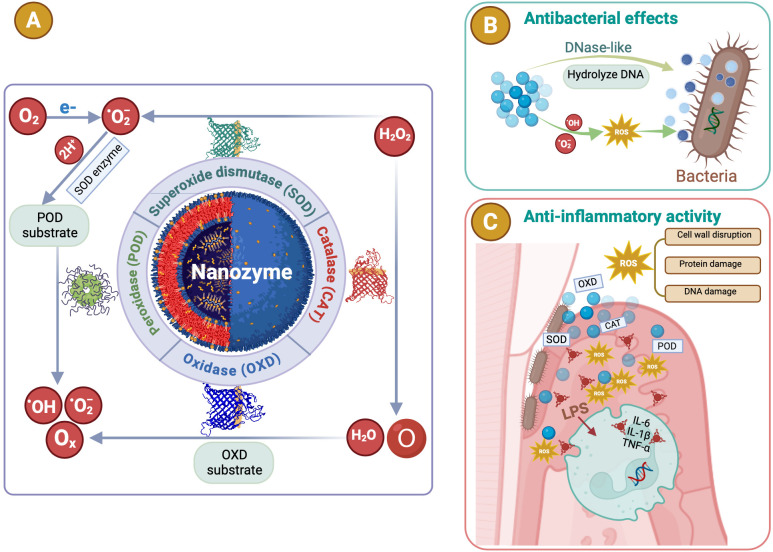
Figure 4.
The antibacterial and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of nanozymes (NZs). (A) NZs are NPs with enzyme-mimicking properties. They mimic enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), oxidase (OXD), and peroxidase (POD). POD or oxidase mimics converting hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) or superoxide (O2) into ROS such as hydroxyl radicals (·OH) or singlet oxygen (1O2). (B) The antibacterial processes and properties of NZs. Catalytic activities of NZs efficiently eliminate bacterial biofilms, showing broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity with minimal biotoxicity. (C) Various NZs exhibit antioxidant properties that help regulate ROS. NZs suppressed inflammatory responses by eliminating ROS, while also lowering pro-inflammatory cytokines and boosting anti-inflammatory cytokines.