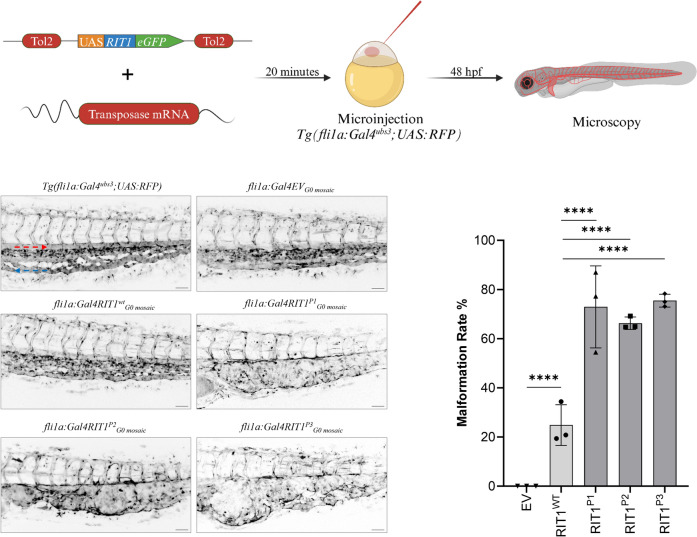
Fig. 3.
Endothelial-specific mosaic expression of RIT1 variants leads to the formation of AVM in zebrafish embryos. a Experimental layout: The plasmid containing human wildtype RIT1 or RIT1 variants, under the control of a UAS element and linked to GFP with a P2A sequence is mixed with transposase mRNA and injected into the one-cell stage of Tg(fli1a:Gal4; UAS:RFP) embryos. Thereafter, embryos are examined at 48 hpf. b Vascular network in the tail of an uninjected Tg(fli1a:Gal4; UAS:RFP), EV and RIT1 variants injected embryos. Arrows represent the direction of arterial and venous blood flow (red and blue arrow, respectively). Note the malformed vasculature with a fusion of the dorsal aorta and the caudal vein as well as dilation of the vessel. Scale bar 50 µm. c Quantification of the vascular anatomy at 48 hpf following the injection of plasmids containing the indicated RIT1 variants, with and without treatment. n = 3. Number of total examined embryos: EV = 66, RIT1WT = 92, RIT1P1 = 67, RIT1P2 = 97, RIT1P3 = 61. Fisher’s exact test, two-tailed. P value ****< 0.0001. Data are presented as mean ± SD. EV empty vector