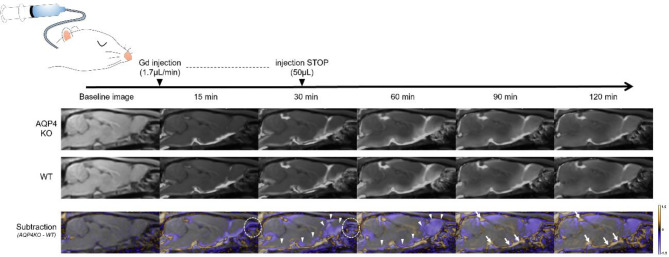
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the experiment and average and subtraction images of intrathecal Gd-tracer changes over time in each group. The signal ratio maps that overlay post-/pre-contrast signal ratio images on the T1-weighted sagittal images of the WT and KO groups are shown in grayscale in the top and middle rows. Each signal ratio map represents the average data for the five rats in each group. The subtraction images, generated by subtracting the signal ratio maps of the WT group from those of the KO group and converting them into color maps with a range of − 1.5 to 1.5, are shown in the bottom row. In the subtraction images, violet indicates a lower signal (i.e., a lower tracer distribution) in the KO group than that in the WT group, and orange indicates the opposite. The KO group had a lower Gd-tracer distribution in the nasal cavity than the WT group (circles). In contrast, the KO group showed a higher Gd-tracer distribution in the ventral and rostral CSF spaces (arrows) than the WT group. In the KO group, the Gd-tracer distribution in the brain surface parenchyma was lower than that in the WT group (arrowheads). Gd, gadolinium-based contrast agents; KO, aquaporin 4 knockout; WT, wild type.