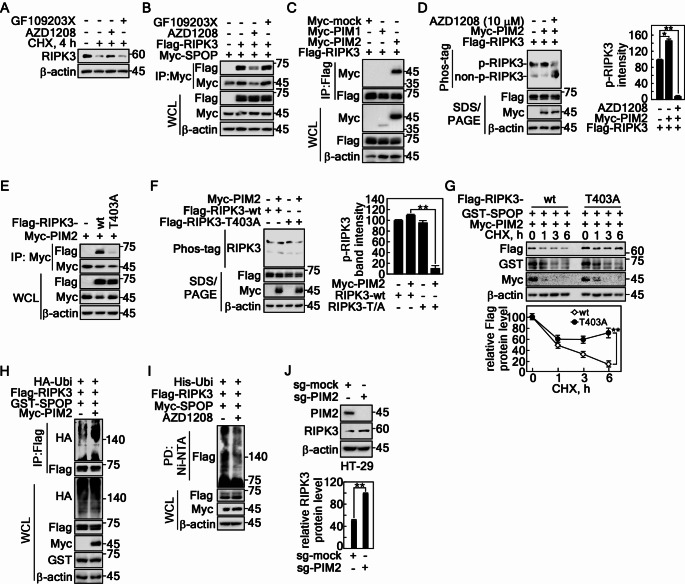
Fig. 5.
PIM2-mediated RIPK3 phosphorylation at Thr403 induces SPOP-mediated RIPK3 destabilization. A PIM inhibition sustained endogenous RIPK3 protein levels, followed by a CHX treatment in HT-29 cells. B PIM inhibition abrogated the interaction between SPOP and RIPK3 in HEK293T cells. C Confirmation of the specific interaction between RIPK3 and PIM2 detected by IP and western blotting in HEK293T cells. D PIM inhibitor abrogated the PIM2-mediated RIPK3 phosphorylation detected by phos-tag gel electrophoresis and western blotting in HEK293T cells. E RIPK3 mutation at Thr403 to Ala abrogated the interaction between SPOP and RIPK3 in HEK293T cells. F RIPK3 mutation at Thr403 to Ala abrogated PIM2-mediate phosphorylation detected by phos-tag gel electrophoresis and western blotting in HEK-293T cells. G SPOP-mediated RIPK3 half-life was prolonged in RIPK3-T403A followed by CHX treatment in HeLa cells. H Coexpression of PIM2 with SPOP and RIPK3 enhanced RIPK3 ubiquitination detected by IP and western blotting in HEK293T cells. I PIM inhibitor abolished SPOP-mediated RIPK3 ubiquitination detected by the Ni-NTA pulldown assay in HEK293T cells. J PIM2 knockout elevated the RIPK3 protein level in sg-PIM2 HT-29 cells. D, F, G and J The error bars from three independent experiments indicate the SEM. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 (Student t-test)