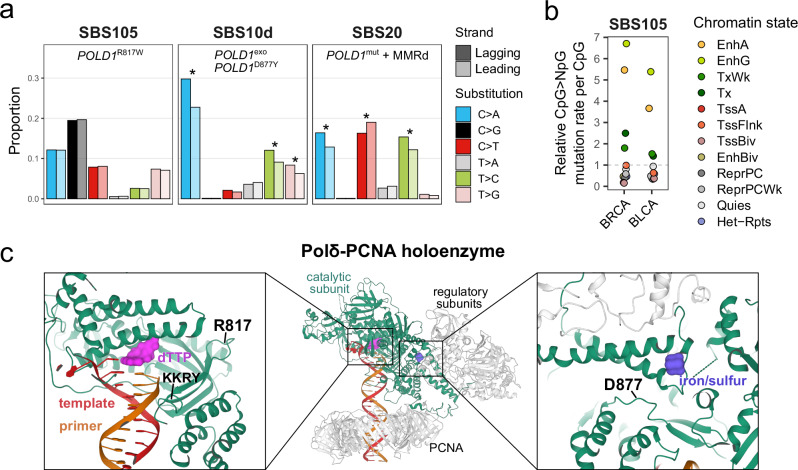
Fig. 2. Features of SBS mutational signatures associated with distinct POLD1 mutations.
a Replication strand asymmetry of mutational signatures associated with POLD1 mutations. The asterisks mark a significant difference in contribution between leading and lagging strands (see “Methods”). POLD1exo*, POLD1 exonuclease domain mutated; POLD1mut, POLD1 mutated; MMRd, mismatch repair deficiency. b SBS105 CpG > NpG relative mutation rates in ENCODE chromatin states of normal cell types matched to each tumor type. BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; BLCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma; EnhA/EnhG, active/genic enhancer; Tx/TxWk, strong/weak transcription; TssA, active TSS; TssFlnk, flanking TSS; TssBiv, bivalent/poised TSS; EnhBiv, bivalent enhancer; ReprPC/ReprPCWk, strong/weak repressed polycomb; Quies, quiescent/low; Het-Rpts, heterochromatin/ZNF genes and repeats. c Pol δ-PCNA holoenzyme structure. Mutated amino acids in the polymerase domain of Pol δ catalytic subunit (POLD1) are indicated in black. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.