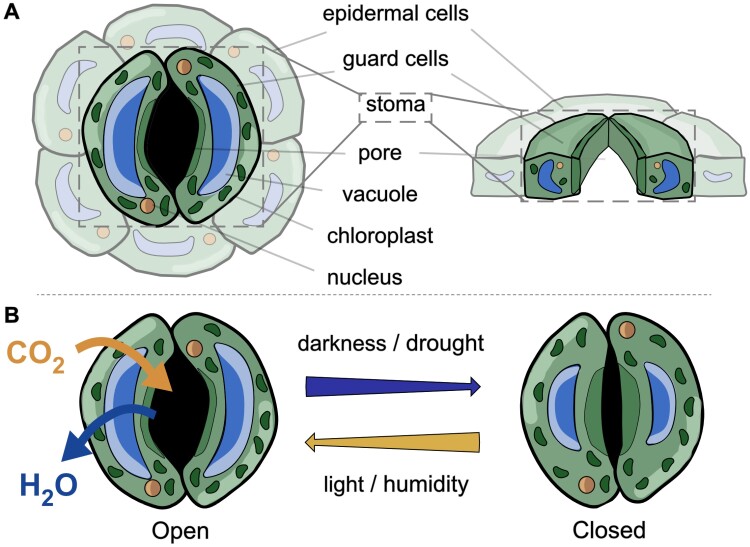
Fig. 1.
Diagram of stomatal structure and function in facilitating gas exchange—example of a dicot stoma. (A) Surface and transverse view of a stoma, encompassing the guard cells and pore, as denoted by the box, and accompanying epidermal cells (faded out). (B) Internal and external signals confer a structural change in the stoma to permit gas exchange when the structure is open, and restrict exchange when closed.