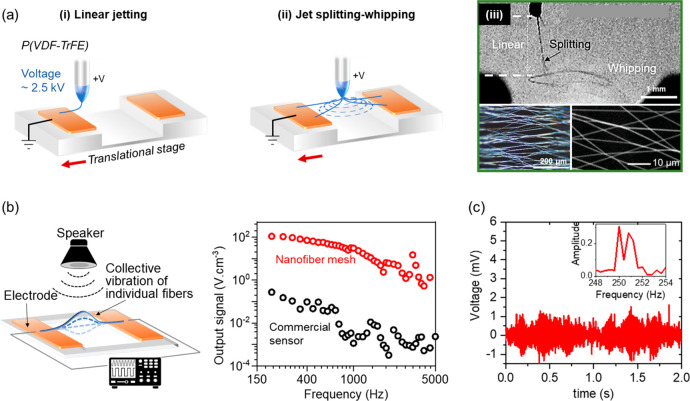
Figure 3.
Process of dNFES and the piezoelectric nanofiber meshes as broadband acoustic sensors. (a) The process of dNFES is composed of (i) linear jetting and (ii) a transient process of jet splitting-whipping. (iii) A photo showing the jet splitting-whipping and microscopic images showing the suspended nanofiber meshs. (b) A schematic illustration of the sound sensing setup and the acoustic sensing bandwidth of the nanofiber mesh (equivalent film thickness ∼ 60 nm) compared with a commercial piezoelectric acoustic sensing dish (300 μm thick). (c) Signal output of the nanofiber mesh at 250 and 251 Hz at 70 dB and the FFT processed spectrum. Reprinted with permission from ref (35). Copyright 2020 John Wiley and Sons.