Figure 7.
Representative AEs constructed by 3D bioprinting
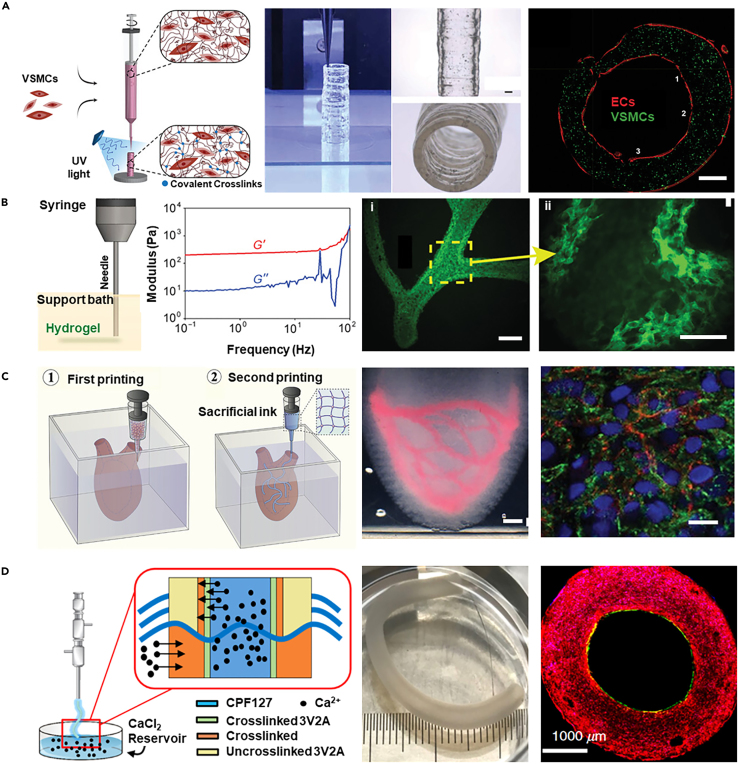
(A) Utilizing a high-viscosity colloidal nanoengineered bioink encapsulating VSMCs, cylindrical blood vessels were printed using layer-by-layer 3D bioprinting technology, followed by seeding with ECs to form the vascular construct (scale bar 2.5 mm). Copyright 2021, Wiley, Reproduced with permission.160
(B) Gelatin, serving as a thermo-reversible support bath material that does not negatively impact cell integration, was rheologically analyzed to exhibit Bingham plastic properties, enabling the printing of an arterial tree structure with alginate hydrogel that features well-defined internal lumens and bifurcations (scale bar i: 2.5 mm, ii: 1 mm). Copyright 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science, Reproduced with permission.162
(C) Sequential suspension 3D bioprinting technology employs MB bioink as a support matrix to facilitate the embedding printing of free-form vascular networks using a HUVECs-enriched sacrificial gelatin bioink (scale bar i: 2 mm, ii: 10 μm). Copyright 2023, Wiley Blackwell, Reproduced with permission.163
(D) Utilizing a bioink containing HUVECs and HAoSMCs, along with a triple coaxial 3D bioprinting, a biomimetic vascular graft with distinct endothelial and muscular layers is directly constructed (scale bar 1000 μm). Copyright 2019, AIP Publishing, Reproduced with permission.15