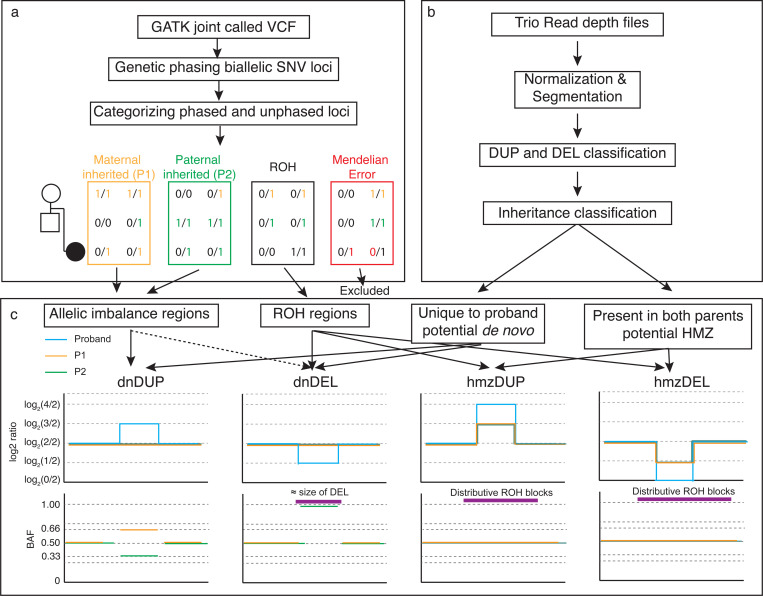
Fig. 1. Overview of Integrating BAF and CNV Analysis Using VizCNV.
a) Demonstrates the methodology for trio-based joint calling and the classification of B-alleles. b) Outlines the approach for analyzing log2 ratios and categorizing CNVs. c) Illustrates the combined analysis and visualization process using phased BAF and log2 ratio data for de novo duplication and deletion, homozygous duplication and deletion (left to right). For a de novo duplication occurring on the maternal allele, we would expect a log2 ratio of log2(3/2) in the proband’s read depth plot, accompanied by phased BAF values of approximately 0.66 for SNVs phased to the maternal allele and 0.33 for those phased to the paternal allele. For a de novo deletion on the maternal allele, we would anticipate a log2 ratio of log2(1/2) in the proband’s read depth plot, with the paternal phased BAF near 1, resembling a ROH similar in size to the deletion, or an allelic imbalance pattern if the deletion is mosaic. In the case of a homozygous duplication, we would expect a log2 ratio of log2(3/2) in both parents and log2(4/2) in the proband, with the duplication overlapping a larger ROH region. For a homozygous deletion, the expected log2 ratio would be log2(1/2) in both parents, with no signal in the proband, and the deletion would overlap a larger ROH region.