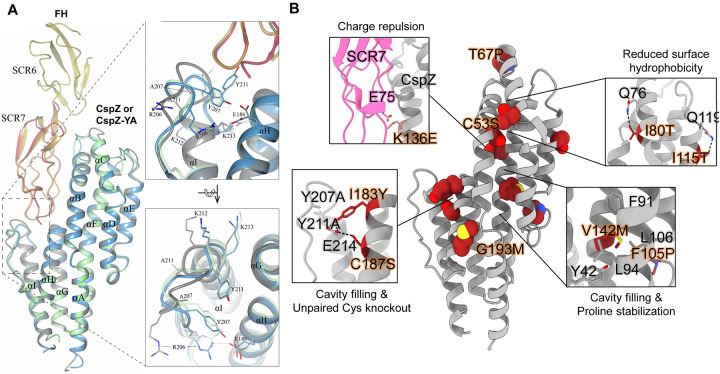
Figure 1. The high-resolution structure of CspZ-YA and the mutagenesis of amino acid residues in CspZ-YA by structure-based vaccine design.
(A) The crystal structure of CspZ-YA (gray; PDB ID 9F1V; rmsd 1.9 Å) is superimposed with the structure of B. burgdorferi B31 CspZ (blue) from the CspZ/SCR6–7 (gold) complex (PDB ID 9F7I; rmsd 0.9 Å) and B. burgdorferi B31 CspZ (green) from the CspZ/SCR7 (red) complex (PDB ID 6ATG; rmsd 0.74 Å). The inlet figures show the loop region between helices H and I, highlighting residues Y207 and Y211 in CspZ from B. burgdorferi strain B31 and the mutated residues A207 and A211 in CspZ-YA. Residues K212 and K213 found in the loop region in CspZ and in the extended helix I in CspZ-YA are shown. The interaction between residues R206 and E186 in CspZ is further indicated. The structure is presented from top and side views. (B) Design landscape of CspZ-YA (PDB ID 9F1V) shown as a ribbon diagram with the side chains of the mutated amino acid residues shown as spheres. Insets highlight the position and side chains of selected stabilizing mutations. Side chains in each inset are shown as dark red sticks with sulfur atoms in yellow, nitrogen atoms in blue and oxygen atoms in red.