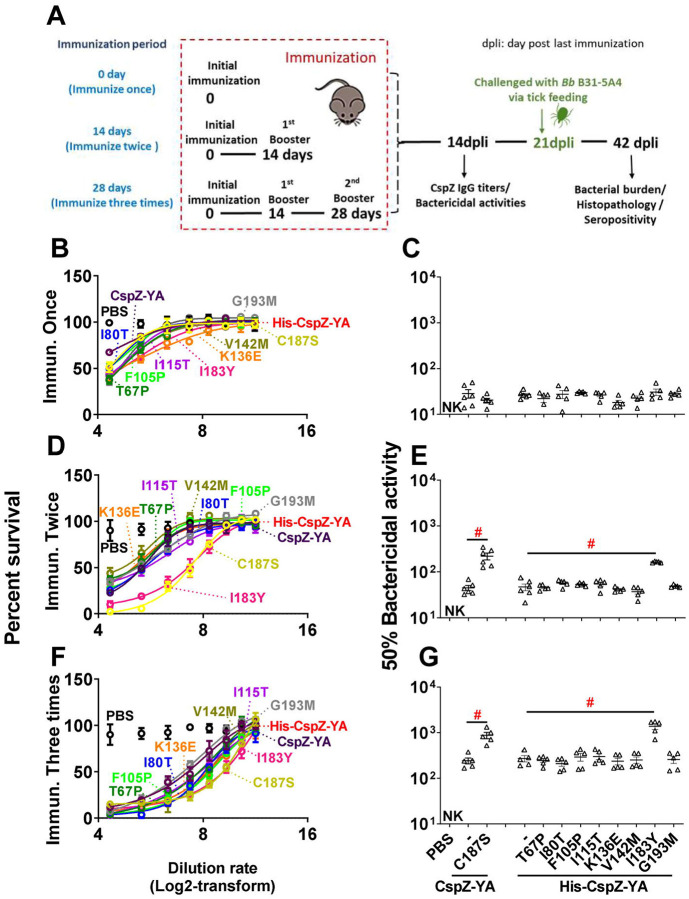
Figure 2. Mice immunized twice and three times with CspZ-YAC187S or CspZ-YAI183Y had sera with more robust levels of borreliacidal activity than CspZ-YA-vaccinated mice.
(A) C3H/HeN mice received an inoculation with PBS (control) or immunization with CspZ-YA or the mutant proteins derived from this protein formulated with TitierMax Gold (TMG) at 0 day for the group of mice that were immunized once. The second group of mice that were immunized twice received the abovementioned proteins or PBS at 14 days after the initial immunization (dpii). The third group of mice that were immunized three times received the abovementioned proteins or PBS at 14 and 28 dpii. At 14 days post last immunization (14dpli), sera from these mice were collected for analyses of the titers of CspZ IgG and bactericidal activities. At 21 dpli, nymphal ticks carrying B. burgdorferi B31-A3 were placed on those mice and allowed to feed until repletion. Mice were sacrificed at 42 dpli for seropositivity, histopathology, and bacterial burden quantification. Mice inoculated with PBS and not fed on by nymphs were included as an uninfected control group. (B to G) Sera were collected at 14 dpli from C3H/HeN mice immunized (B and C) once, (D and E) twice, or (F and G) three times. These mice were immunized with PBS (control) or untagged CspZ-YA or its derived mutant proteins, or histidine tagged CspZ-YA (His-CspZ-YA), or its derived mutant proteins (Six mice for CspZ-YA- or CspZ-YAC187S-immunized mice whereas five mice for the rest of immunization groups of mice). These sera were serially diluted as indicated, and mixed with guinea pig complement and B. burgdorferi B31-A3 (5 × 105 cells ml−1). After being incubated for 24 hours, surviving spirochetes were quantified from three fields of view for each sample using dark-field microscopy. The work was performed on three independent experiments. (A, C, and E) The survival percentage was derived from the proportion of serum-treated to untreated spirochetes. Data shown are the mean ± SEM of the survival percentage from three replicates in one representative experiment. (B, D, and F) The % borreliacidal dilution of each serum sample, representing the dilution rate that effectively killed 50% of spirochetes, was obtained from curve-fitting and extrapolation of Panel A, C, and E. Data shown are the geometric mean ± geometric standard deviation of the borreliacidal titers from three experiments. The exact values are shown in Table S1. PBS-inoculated mouse sera displayed no bactericidal activity (“NK”, no killing). Statistical significance (p < 0.05, Kruskal Wallis test with the two-stage step-up method of Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli) of differences in borreliacidal titers between groups are indicated (“#”).