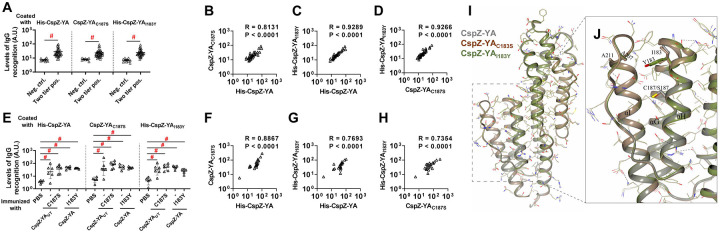
Figure 4. CspZ antibodies originating from humans or mice recognized CspZ-YAC187S or CspZ-YAI183Y at indistinguishable levels from CspZ-YA.
(A to D) Sera from 36 patients with both seropositive for Lyme disease (“Two tier positive”; Positive in two tier test) in Fig. S4 were included. (A) These sera were applied to determined their levels of recognition to histidine tagged CspZ-YA (His-CspZ-YA) or CspZ-YAI183Y (His-CspZ-YAI183Y), or untagged CspZ-YAC187S or using ELISA as described in the section “ELISA” in Materials and Methods. Ten serum samples from humans residing in non-endemic area of Lyme disease were included as negative control. Data shown are the geometric mean ± geometric standard deviation of levels of recognition in each group of serum samples. Statistical significance (p < 0.05, Kruskal Wallis test with the two-stage step-up method of Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli) of differences in levels of recognition by groups are indicated (“#”).(E to H) Sera from five histidine tagged His-CspZ-YA or CspZ-YAI183Y (I183Y)-, or six untagged CspZ-YA- or CspZ-YAC187S (C187S)-immunized C3H/HeN mice that were immunized twice in the fashion described in Fig. 1 were collected at 14dpli. PBS-inoculated mice were included as control. For each serum sample, the levels of its recognition by histidine tagged CspZ-YA, CspZ-YAC187S or CspZI183Y were measured using ELISA. Data shown are the geometric mean ± geometric standard deviation of levels of recognition. Statistical significance (p < 0.05, Kruskal Wallis test with the two-stage step-up method of Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli) of differences in levels of recognition by groups are indicated (“#”). For each serum sample originated from (B to D) humans or (F to H) mice, the values representing the levels of recognition by (B and F) CspZ-YA vs. CspZ-YAC187S, (C and G) CspZ-YA vs. CspZ-YAI183Y, or (D and H) CspZ-YAC187S vs. CspZ-YAI183Y were plotted. The correlation of these values derived from recognition by each of indicated CspZ-YA proteins was quantitatively determined using Spearman analysis and shown as R values. P values are also shown to demonstrate the statistical significance (p < 0.05, Spearman analysis) of the correlation between indicated values in X- and Y-axis in panel B to D and F to H. (I) Superimposed crystal structures of CspZ-YA (gray; PDB ID 9F1V), CspZ-YAC187S (brown; PDB ID 9F21) and the predicted structure of CspZ-YAI183Y (green). Side chains as thin bonds in all three proteins are illustrated. (J) Shown is the region in CspZ-YA, CspZ-YAC187S and CspZ-YAI183Y where mutations (A207, A211, C187, S187, I183, and Y183) were introduced. Residues associated with mutations are illustrated as thick bonds, but all other residues in all three proteins are represented as thin bonds. All the interactions observed between the amino acid side chains in CspZ-YA are indicated as dotted lines.