Figure 2. Characterization of protein expression during axolotl embryogenesis.
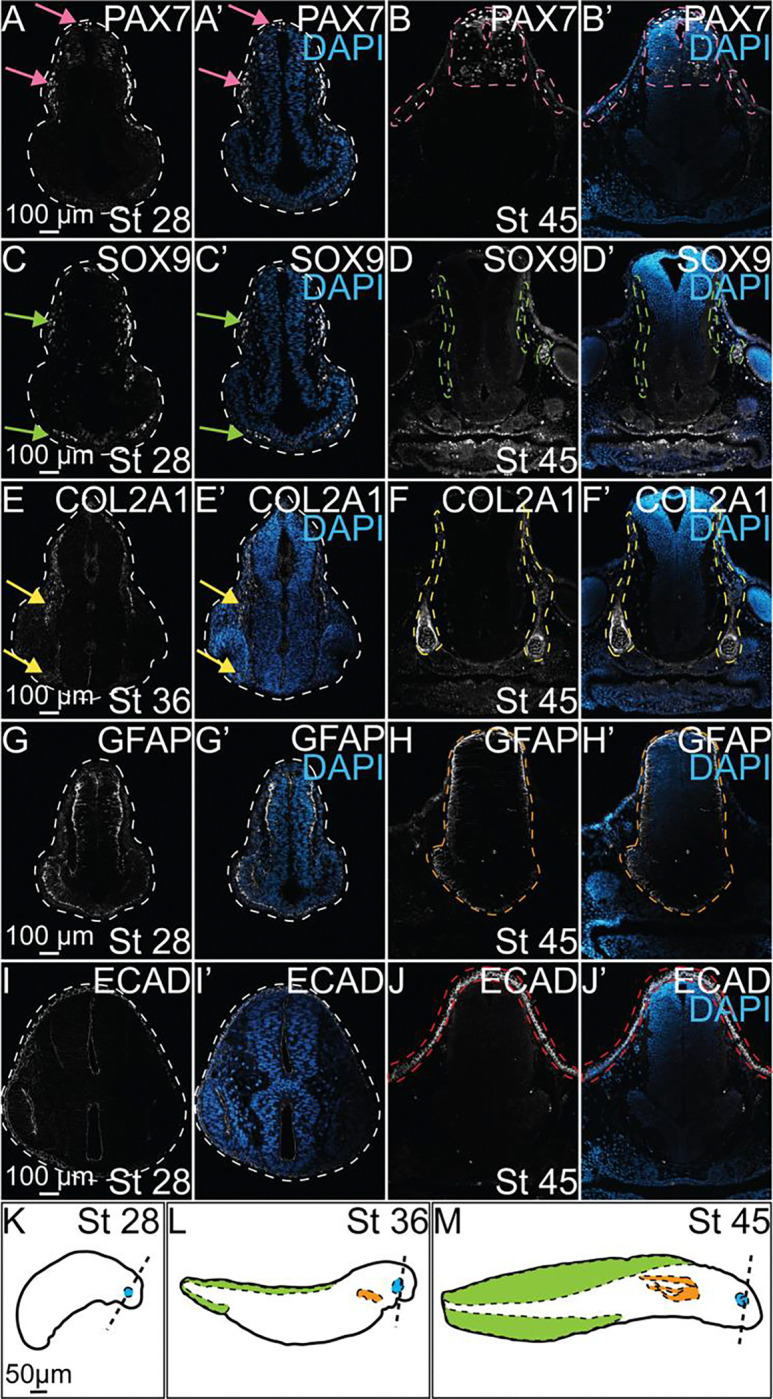
IHC for PAX7 (A-B, A’-B’), SOX9 (C-D, C’-D’), COL2A1 (E-F, E’-F’), GFAP (G-H, G’-H’), and ECAD (I-J, I’-J’) in control axolotl embryos across several stages of development. (A’-J’) IHC for DAPI overlaid with each individual marker to highlight the present anatomical structures at each stage. (A, A’) Pink arrows identify expression of PAX7 in specified NC in the dorsal neural tube and migratory NC. (B, B’) Pink dashed outlines highlight superficial expression of PAX7 in skin and expression in developing interneurons in the NT. (C, C’) Green arrows highight SOX9+ NC, including those beginning to colonize the ventral face. (D, D’) Green dashed outlines identify SOX9 expression surrounding the neural tube and behind the developing eye. (E, E’) Yellow arrows indicate expression of COL2A1 in late migratory NC that follows expression of SOX9 in earlier stages. (F, F’) Yellow dashed outlines highlight COL2A1 expression in the early formation of the cranial cartilages. (H, H’) The orange dashed outline identifies the developing neural tube and expression of GFAP in glial progenitors. (J, J’) The red dashed outlines highlights expression of ECAD in epithelial cells of the developing skin. (K-M) Drawings of axolotl embryos at stages 28, 36, and 45 in development. Dashed lines approximate the axial level in the head at which transverse section images were taken. Developing ocular structures, gills, and dorsal fin are highlighted in blue, orange, and green, respectively.
