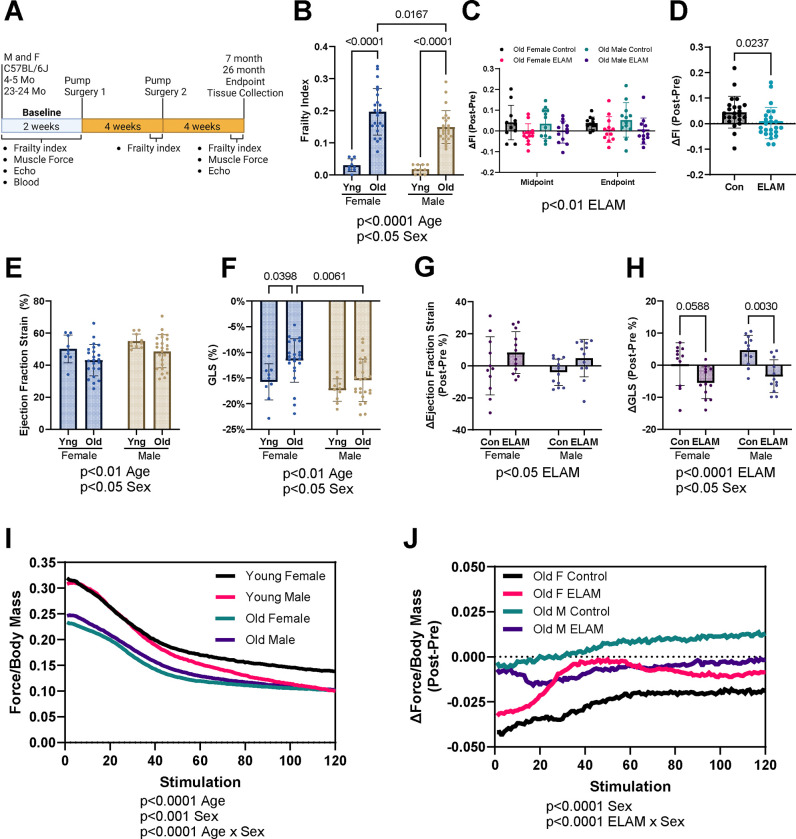
Figure 1: Effect of 2-months ELAM treatment on frailty, cardiac function, and muscle force.
A. Experimental design. B. Baseline frailty index (FI) of young (Yng) and old mice. C. Delta (Δ, Post-pre) FI at midpoint (4 weeks) and endpoint (8 weeks) for old mice. D. Combined Δ frailty index at endpoint for control (Con) and elamipretide (ELAM) treated male and female old mice. E. Baseline ejection fraction determined and F. Global longitudinal strain (GLS) from strain analysis of parasternal long axis images of the left ventricle (LV) of young and old mice. G. Δ ejection fraction and H. GLS determined using strain analysis at endpoint for old mice. I. Baseline in vivo muscle force normalized to body mass during repeating fatigue stimulations in young and old mice. J. Δ in vivo muscle force normalized to body mass during repeating fatigue stimulations at endpoint for old mice. 4–5-month-old (young) female and male (n=9–10) and 23–24-month-old (old) female (n=23–24) and male were compared for each measurement at baseline. ELAM treatment effects were compared in control and ELAM-treated old mice (n=11–12) using Δ measurements. Only mice that survived to study endpoint were included in the analysis. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, except for in vivo muscle fatigue and ΔFI which were determined by three-way ANOVA. Combined ΔFI significance determined by student’s t-test. Significant ANOVA factors written in text with selected Tukey’s post hoc test comparisons on graphs. Error bars represent sample means ± standard deviations; error bars omitted from I., J. for clarity.