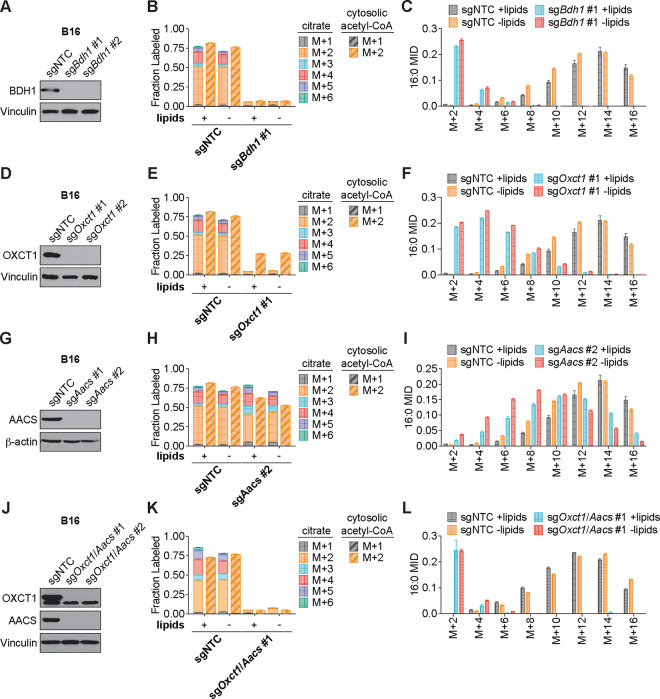
Figure 3. β-OHB can contribute to fatty acid synthesis through a citrate-independent route that requires AACS.
A, Immunoblot for BDH1 and vinculin in the indicated B16 knockout lines. NTC, non-targeting control. B, C, Citrate (solid bars) and cytosolic acetyl-CoA (dashed bars) MIDs (B), and 16:0 MID (C) in B16 sgNTC versus sgBdh1 #1 cells labeled with [U-13C]-β-OHB for 48 h in lipid-replete versus lipid-depleted culture media. D, Immunoblot for OXCT1 and vinculin in the indicated B16 knockout lines. E, F, Citrate (solid bars) and cytosolic acetyl-CoA (dashed bars) MIDs (E), and 16:0 MID (F) in B16 sgNTC versus sgOxct1 #1 cells labeled with [U-13C]-β-OHB for 48 h in lipid-replete versus lipid-depleted culture media. G, Immunoblot for AACS and β-actin in the indicated B16 knockout lines. H, I, Citrate (solid bars) and cytosolic acetyl-CoA (dashed bars) MIDs (H), and 16:0 MID (I) in B16 sgNTC versus sgAacs #2 cells labeled with [U-13C]-β-OHB for 48 h in lipid-replete versus lipid-depleted culture media. J, Immunoblot for OXCT1, AACS, and vinculin in the indicated B16 knockout lines. K, L, Citrate (solid bars) and cytosolic acetyl-CoA (dashed bars) MIDs (K), and 16:0 MID (L) in B16 sgNTC versus sgOxct1/Aacs #1 cells labeled with [U-13C]-β-OHB for 48 h in lipid-replete versus lipid-depleted culture media. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m; n = 3 biologically independent replicates.