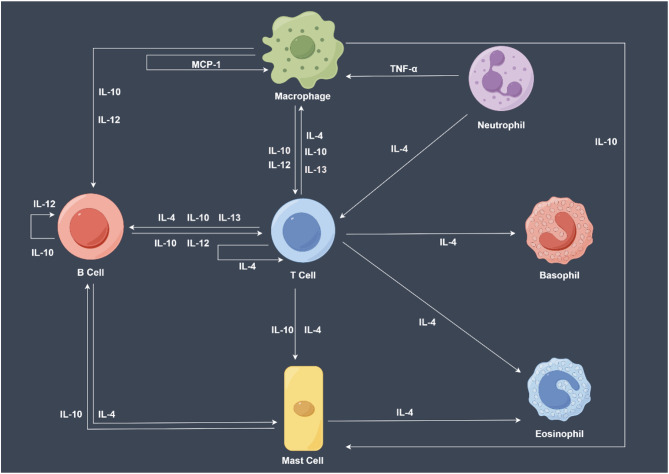
Fig. 1.
Overview of the production of some cytokines. IL-4 is an adaptive cytokine primarily secreted by Th2 cells, mast cells, and eosinophils. IL-4 plays a pivotal role in regulating humoral immunity, promoting IgG and IgE production, enhancing the proliferation and differentiation of B cells, and suppressing Th1 cell-mediated inflammatory responses. IL-10 is a cytokine with extensive anti-inflammatory properties that is secreted by various cell types, including T cells, B cells, macrophages, and certain dendritic cells. IL-10 effectively inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and limits autoimmune responses, thus playing a crucial role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing immunopathological damage. IL-12 is produced by dendritic cells, macrophages, and certain B cells, and is essential for the differentiation and activation of Th1 cells. IL-12 is significant in anti-infective immune responses, particularly against intracellular pathogens, and promotes the recruitment and activation of natural killer cells and T cells. IL-13, with biological functions similar to IL-4, is predominantly produced by Th2 cells and contributes to regulating B cell function, enhancing antibody production, and balancing immune responses. (The figure was created using https://www.figdraw.com)